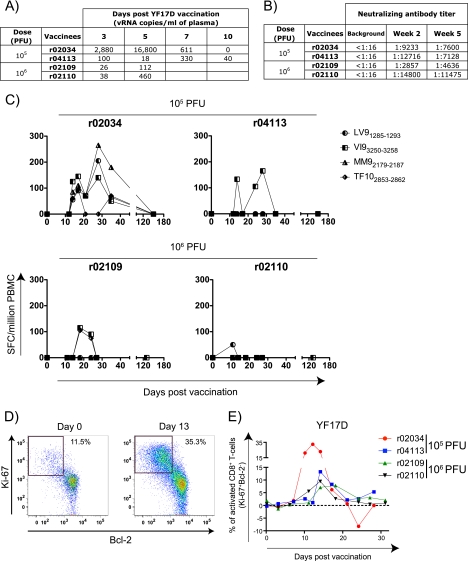
FIG. 1.
YF17D replicates and induces neutralizing antibodies, virus-specific CD8+ T cells, and the activation of CD8+ T cells in rhesus macaques. (A) Replication of YF17D during the first 10 days after vaccination with two different doses, as measured by quantitative PCR (Q-PCR) using the following primers: forward primer YF-17D 10188 (5′-GCGGATCACTGATTGGAATGAC-3′), reverse primer YF-17D 10264 (5′-CGTTCGGATACGATGGATGACTA-3′), and probe 6-carboxyfluorescein (6Fam)-5′-AATAGGGCCACCTGGGCCTCCC-3′-6-carboxytetramethylrhodamine (TamraQ). (B) Titer of neutralizing antibodies determined at 2 and 5 weeks after YF17D vaccination. (C) Fresh PBMC from vaccinees (100,000 cells/well) were used in IFN-γ ELISPOT assays (41) to assess T-cell responses against YF17D. We used 4 epitopes (LTPVTMAEV [LV91285-1293], VSPGNGWMI [VI93250-3258], MSPKGISRM [MM92179-2187], and TTPFGQQRVF [TF102853-2862]) predicted to bind to Mamu-A*01 as defined by the MHC pathway algorithm (31). All IFN-γ ELISPOT results were considered positive if they were ≥50 SFC/106 PBMC and ≥2 standard deviations over the background. (D) Identification of activated CD8+ T cells after vaccination with YF17D based on the expression of the proliferation and proapoptotic markers Ki-67 and Bcl-2, respectively (26). We stained whole blood cells with antibodies against CD3 and CD8. We then permeabilized and subsequently labeled these cells with Bcl-2- and Ki-67-specific antibodies. The flow graphs were gated on CD3+ CD8+ lymphocytes. (E) Expression kinetics of Ki-67 and Bcl-2 in CD8+ T cells after vaccination with YF17D.