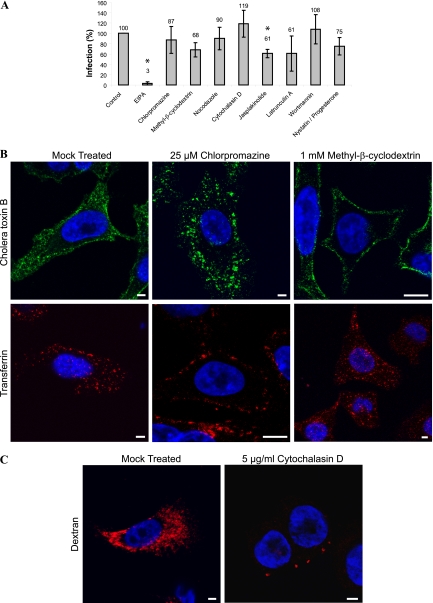
FIG. 1.
Effects of endocytosis inhibitors on CAV9 infection on A549 cells. (A) A549 cells were preincubated at 37°C for 30 min with EIPA (100 μM), chlorpromazine (25 μM), methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβC; 1 mM), nocodazole (33.2 μM), cytochalasin D (5 μg/ml), jasplakinolide (2 μM), latrunculin A (1 μM), wortmannin (100 nM), or with a combination of nystatin (25 μg/ml) and progesterone (10 μg/ml). The cells were infected with CAV9 at 60% efficiency of infection and incubated on ice for 1 h. The unbound virus was removed, and cells were transferred to 37°C and incubated for 6 h. The inhibitors were present throughout the experiment. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with Hoechst and virus-specific antibody, and the efficiency of infection was calculated from confocal images as the ratio of infected cells to the total cell number. The experiment was performed three times, and the mean is shown. Statistical significance was calculated with a paired-sample t test, in which a P of <0.05 was considered significant. Inhibitors showing a statistically significant effect are shown with an asterisk. Effects of chlorpromazine (25 μM) and MβC (1 mM) on the internalization of cholera toxin B and transferrin (B) and of cytochalasin D (5 μg/ml) on the internalization of dextran (C) are shown. A549 cells were incubated with the inhibitors for 30 min at 37°C, after which AF 488-conjugated cholera toxin B (0.2 μg/ml), AF 546-conjugated transferrin (10 μg/ml), or AF 546-conjugated dextran (250 μg/ml) was added. The incubation was continued for 15 min, the cells were fixed and stained with Hoechst, and confocal images were taken. Cholera toxin B is shown in green, transferrin and dextran are in red, and nuclei are in blue. Bar, 10 μm.