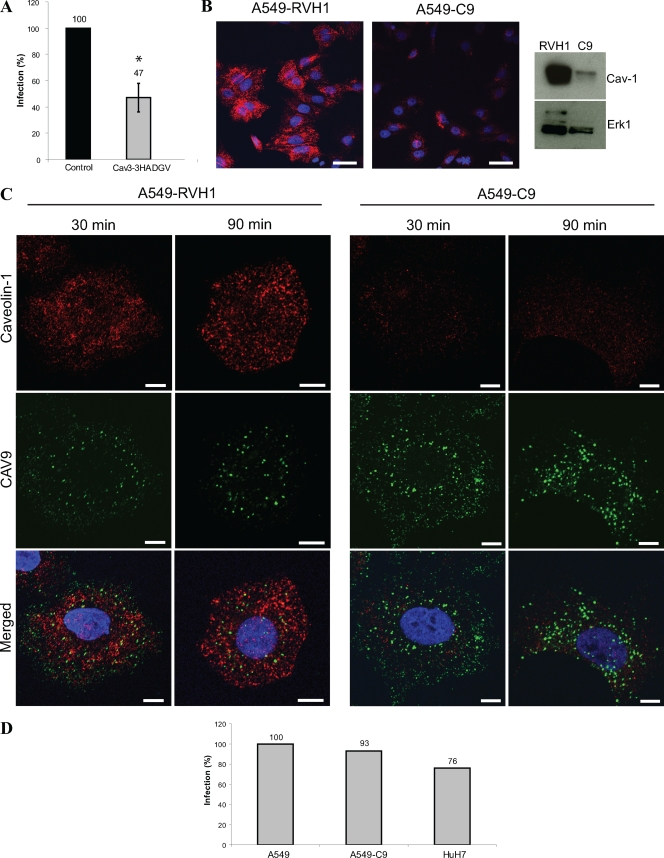
FIG. 6.
Caveolin-1 is not needed for CAV9 infection. (A) Plasmid constructs expressing wild-type and dominant negative caveolin-3 were transiently transfected to A549 cells. After 48 h, the cells were infected with CAV9 at 60% efficiency of infection, incubated on ice for 1 h, and washed. Warm medium was added, and the cells were transferred to 37°C. The cells were incubated for 6 h prior to fixation and staining. Infection efficiency was counted from microscopic images of 100 to 200 transfected cells in three separate experiments, and the infection in wild-type control cells was set to 100%. Error bar indicates SD. (B) The caveolin-1-silenced cell line A549-C9 was generated by infecting A549 cells with retrovirus vector carrying caveolin-1-silencing shRNA. The vector RVH1 was used as a control. The silencing efficiency was analyzed by confocal imaging and Western analysis. For confocal imaging, the cells were cultured for 24 h on coverslips, fixed, and permeabilized, after which caveolin-1 was stained with rabbit polyclonal antiserum and AF 546-labeled secondary antibody (red). For Western analysis, protein samples (30 μg) were separated in a 15% SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to a Hybond-P membrane. Caveolin-1-specific antibody combined to HRP-labeled secondary antibody was used for detection, and Erk1-specific antibody was used as a loading control. (C) Cell lines A549-RVH1 and A549-C9 were infected with CAV9 as above. The infection was allowed to proceed for 30 or 90 min before fixation, permeabilization, and immunostaining. CAV9 is shown in green, caveolin-1 is in red, and nuclei are in blue. Bar, 10 μm. (D) A549, A549-C9, and HuH-7 cells were infected with CAV9 as above. After 6 h of incubation at 37°C, cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with CAV9-specific antibody. Infection efficiency was counted from microscopic images of 100 to 200 cells, and the infection in A549 cells was set to 100%.