Figure 1.
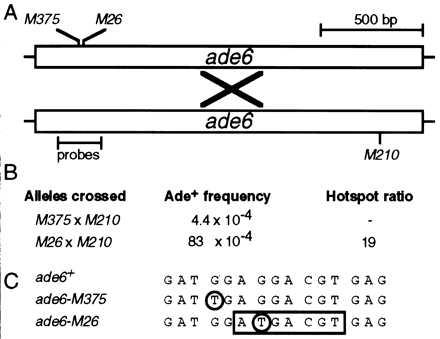
Hotspot activity of M26. (A) Schematic diagram of the ade6 gene showing positions of alleles and probes used for gel mobility shift experiments. Meiotic recombination (×) between a chromosome harboring the ade6-M26 or the ade6-M375 allele and a chromosome with the ade6-M210 allele generates a wild-type, selectable ade6+ gene. (B) Example of M26 recombination hotspot activity. Data are from Table 2. Recombination in test crosses containing M26 is increased up to 20-fold relative to recombination when using another allele, such as M375 (5). (C) DNA sequence surrounding the ade6-M26 recombination hotspot (7, 13). Both M375 and M26 are identical single base pair substitutions (circled) that generate stop codons. The M26 mutation creates a 7-bp site (box) that is bound by the Mts1/Mts2 heterodimer (15) and is required for hotspot activity in vivo (14).
