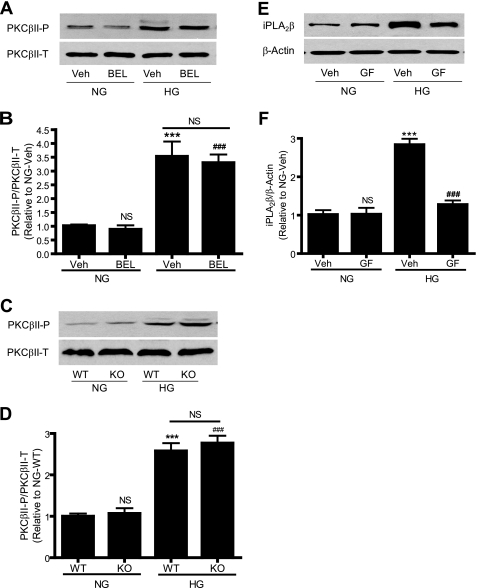
FIGURE 2.
BEL inhibition or genetic deletion of iPLA2β does not affect high glucose-induced PKCβII phosphorylation, whereas inhibition of PKC attenuates high glucose-induced iPLA2β protein up-regulation. 70–80% confluent rat (A, B, E, and F) and mouse (C and D) aortic VSMC were incubated with 10% FBS medium containing NG or HG in the presence of BEL (3 μm) for 24 h (A and B), GF109203X (GF, 3 μm) for 12 h (E and F), and vehicle (Veh, Me2SO), respectively. A, C, and E, representative Western blots of iPLA2β, total PKCβII (PKCβII-T), and phosphorylated PKCβII (PKCβII-P); B, D, and F, summary of data shown in A, C, and E, respectively. Each experiment was repeated at least three times. ***, p < 0.001 versus NG/vehicle in B, NG/WT in D, and NG/vehicle in F; ###, p < 0.001 versus NG/vehicle in B, NG/WT in D, and HG/vehicle in F; NS, not significant, HG/vehicle versus HG/BEL in B; HG/WT versus HG/KO in D.