Figure 1.
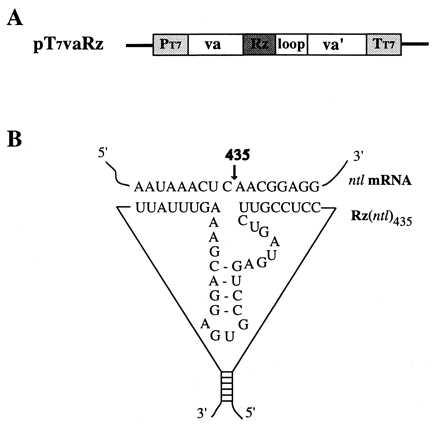
The ntl ribozyme expression vector and schematic secondary structure of ntl ribozyme RNA. (A) Ntl ribozyme expression vector pT7vaRz. The vector pT7vaRz(ntl) was constructed first by an insertion of a ribozyme sequence (Rz) against the ntl mRNA into a va I RNA expression cassette; the cassette containing the ribozyme sequence (va-Rz-loop-va’) subsequently was cloned into a pTM-1 expression vector (27) lacking the encephalomyocarditis virus internal ribosome entry site sequence in such a way that the expression of Rz is under the control of both a T7 promoter (PT7) and an adenovirus va I internal promoter, a pol III promoter (upstream va). The PT7-driven transcription stops at the T7 terminator (TT7) whereas the va I-driven transcription terminates at the 3′ end of the loop. (B) The sequences flanking Rz(ntl) were designed in such a way that the 5′ and 3′ ends of the ntl ribozyme form a stable stem structure (18). Both the ribozyme and its targeted, complementary ntl mRNA sequences, as well as the cleavage site (435), also are shown.
