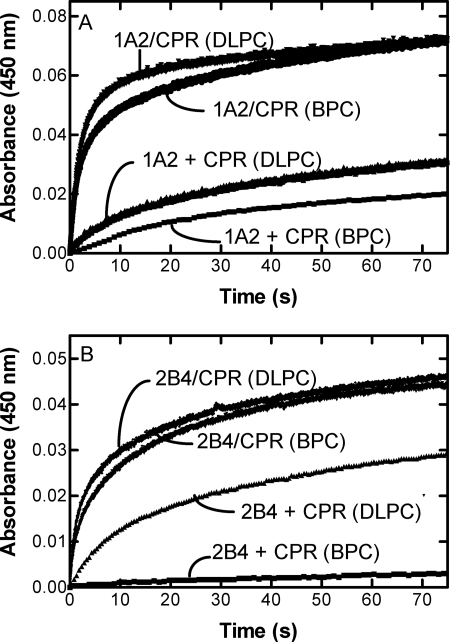
FIGURE 2.
Effect of mixing of CPR-containing and P450-containing vesicles; comparison of BPC and DLPC systems. The scans were generated by measuring the anaerobic reduction of CYP1A2-containing (A) or CYP2B4-containing vesicles (B) by CPR when the enzymes were reconstituted together (CPR/P450) or separately (CPR + P450) in phospholipid (either BPC or DLPC, as indicated). When CPR and P450 were reconstituted separately in phospholipid, each reconstituted system was placed in separate syringes of the stopped flow spectrophotometer, the NADPH was added to the syringe containing the P450, and the time course of reduction was monitored as described under “Experimental Procedures.” When the NADPH-dependent reduction of the binary system containing CPR, P450, and lipid was measured, the reconstituted system from one arm of the stopped flow spectrophotometer was mixed with a solution of NADPH from the other arm of the instrument as described under “Experimental Procedures.”