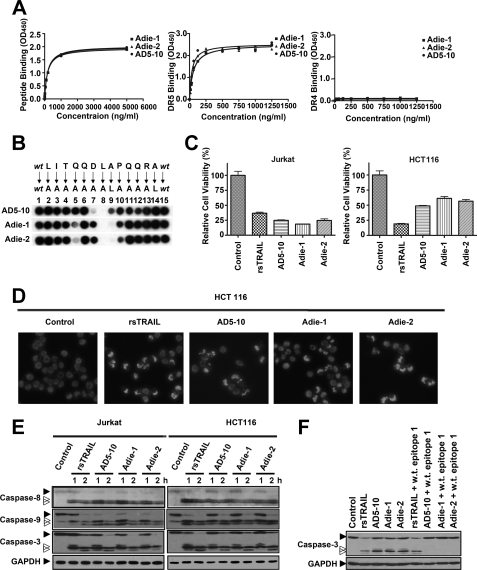
FIGURE 5.
Antibodies against the epitope −1LITQQDLAPQQRA12 possess tumoricidal activities. A, binding affinity of Adie-1 and Adie-2 to the DR5 epitope recognized by AD5-10 (left), soluble DR5-ECD (middle), and soluble DR4-ECD (right). Synthetic immunizing peptide or recombinant soluble DR4/5 was immobilized on a 96-well plate. The plate was then incubated with the indicated concentration of AD5-10, Adie-1, and Adie-2. The binding affinities were then measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Values represent the mean ± S.D. of triplicate samples. B, alanine-scanning mutagenesis analysis of the recognition pattern of anti-DR5 mAbs. An array of peptide −1LITQQDLAPQQRA12 was probed with 0.2 μg/ml AD5-10, Adie-1, or Adie-2, respectively. The first and the last spot corresponded to the parental peptide, whereas the other spots represented an Ala-substituted analogue of wild-type (wt) sequence as indicated above the individual spots. C, tumoricidal function of Adie-1 and Adie-2 compared with AD5-10. Jurkat or HCT116 cells were incubated with 500 ng/ml anti-DR5 mAbs or rsTRAIL for 8 h. Cell viability was determined by a CCK-8 assay. D, Hoechst 33258 staining. HCT116 cells were cultured with 500 ng/ml anti-DR5 mAbs or rsTRAIL for 4 h. After fixation, cells were stained with Hoechst 33258 (1 μg/ml), and nuclear condensation and fragmentation of chromatin were observed by fluorescence microscopy (20×). The excitation wavelength was 380 nm. E, Jurkat cells and HCT116 cells were incubated with 500 ng/ml anti-DR5 mAbs or rsTRAIL for the indicated times. The activation of caspase-8, -9, and -3 was tested using the respective antibodies. F, Western blot analysis of caspase-3 activation in Jurkat cells treated with 500 ng/ml anti-DR5 mAbs or rsTRAIL in the absence or presence of synthetic wild-type epitope for 2 h. All experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.