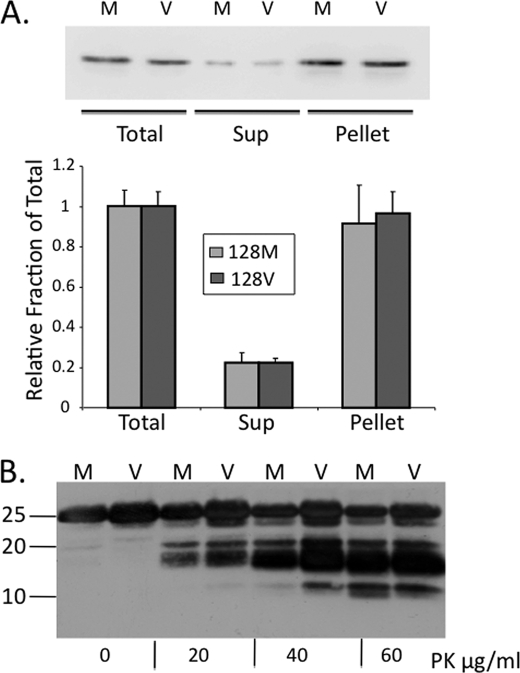
FIGURE 2.
PrP insolubility and PK resistance of PrP-128M and PrP-128V in the yeast cytosol. A, yeast cells expressing mouse sequence PrP-128M and PrP-128V were lysed in TEN buffer containing 10% Sarkosyl, from which equal aliquots of the total, supernatant (Sup), and pellet fractions, following 16,000 × g centrifugation, were subjected to Western analysis. PrP was probed with the C-terminal anti-mouse PrP F(ab) R1 antibody (residues 225–231). Solubility profile of each PrP was determined as the relative density of the supernatant signal relative to the total signal from each of 3 assays, using a Bio-Rad Alpha Document Imager and Quantity One® (Bio-Rad) software. The pellet represents nearly 90% of the fraction, suggesting rapid conversion of newly synthesized soluble PrP to the insoluble aggregate. B, Western blot of PrP-128M (M) and PrP-128V (V) expressed in the yeast cytosol and treated with PK (0 to 60 μg/ml) for 1 h at 37 °C. Prominent PK-resistant fragments of ∼18–20 kDa are observed at all concentrations of PK, although smaller fragments appear with higher concentrations. No major differences in conformational subtype were demonstrated by this assay.