FIGURE 1.
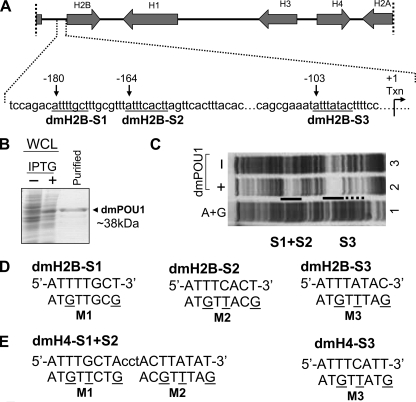
Three pivotal octamer elements for the Pdm-1 anchorage to the dmH2B promoter. A, depicted on top is a D. melanogaster histone genes cluster (∼5 kb) on chromosome 2L, with transcriptional directions of the genes indicated by arrows. Illustrated below are details of the dmH2B promoter, with octamer positions (relative to the transcription start site) indicated with arrows, and sequences (from distal to proximal, dmH2B-S1, dmH2B-S2, and dmH2B-S3) underlined. B, shown is bacterially expressed GST-Pdm-1 POU domain fusion protein (dmPOU1). Whole cell lysates (WCL) of the host XA90 Escherichia coli strain from the control and isopropyl 1-thio-β-d-galactopyranoside-induced samples were assessed for protein production (staining of the SDS-gel-resolved proteins with Coomassie Blue). Lane 3 shows the purified protein. C, shown is a footprint analysis of the promoter region of the dmH2B gene without (lane 3) or with 1 μg dmPOU1 (lane 2). The protected regions that cover dmH2B-S1, -S2, and -S3 sites are indicated. D, sequences of the dmH2B-S1, -S2, and -S3 octamer sites (uppercase) are shown. Oligonucleotides encompassing individual sites were end-labeled with 33P and used in EMSAs. Base-substituted oligonucleotides (M1, M2, and M3) are indicated with mutated residues underlined. E, sequences of the dmH4-S1+S2 and -S3 octamer sites (uppercase) are shown. Base-substituted oligonucleotides (M1, M2, and M3) are indicated with the mutated residues underlined. These oligonucleotides were used in later EMSAs (Fig. 6C).