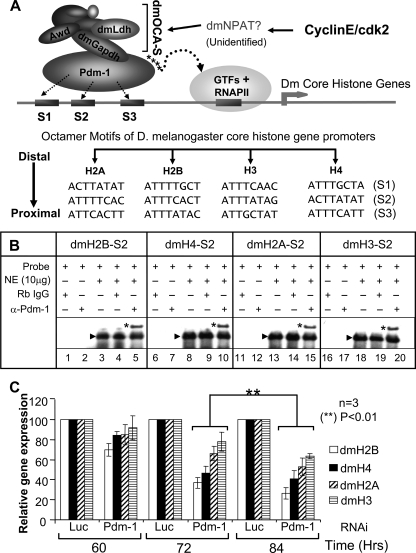
FIGURE 7.
Pdm-1 as a universal transcription factor connecting dmOCA-S to Drosophila core histone gene promoters. A, shown is a transcriptional regulation pathway of D. melanogaster core histone genes. All the core histone genes contain multiple octamer sites in their promoters for recruitment of the common transcription factor Pdm-1, which in turn recruits dmOCA-S that might well be the universal co-activator for the coordinated expression of all Drosophila core histone genes. B, EMSAs analyses are shown using crude nuclear extract (NE) and oligos containing the H2B, H4, H2A, and H3 S2 sites, which formed one major complex (arrowhead; lanes 3, 8, 13, and 18). Naïve rabbit IgG as control did not supershift the complex formed between nuclear extract and probe (lanes 4, 9, 14, and 19); however, rabbit anti-Pdm-1 antibodies produced a supershifted complex (*), hence, demonstrating that the complex contained native endogenous Pdm-1 transcription factor (lanes 5, 10, 15, and 20). Note that, for space considerations the images of the gel portions containing free probes are not shown here as well as in the EMSAs in Figs. 2 and 6. C, core histone gene expression in a time course is shown. Schneider-2 (S2) cells were treated with 37 nm luciferase- or Pdm-1-specific dsRNA and harvested at 60, 72, and 84 h for expression analyses of dmH2A, dmH2B, dmH3, and dmH4 core histone genes using quantitative RT-qPCR.