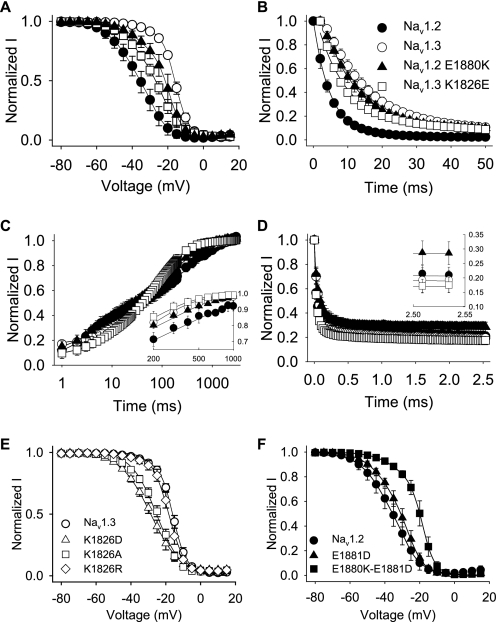
FIGURE 6.
Fast inactivation properties regulated by a single carboxyl-terminal residue. A, the voltage dependence of inactivation for Nav1.3 K1826E (squares) and Nav1.2 E1880K (triangles) is shown compared with the corresponding Nav1.3 (white circles) and Nav1.2 (black circles) wild-type channels. The parameters of the fits and sample sizes are shown in Table 3. B, normalized current versus the depolarization time is shown for entry into inactivation, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The parameters of the fits and sample sizes are shown in Table 3. C, recovery from inactivation was determined using three two-pulse protocols and fitted as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Inset, recovery is shown for time points between 200 and 1000 ms on a linear scale. Sample sizes were 9 for Nav1.2, 6 for Nav1.3, 5 for Nav1.2 E1880K, and 11 for Nav1.3 K1826E. D, use-dependent inactivation was analyzed at 39 Hz as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Inset, entry rate is shown for the last two time points in the protocol. Sample sizes were 9 for Nav1.2, 6 for Nav1.3, 5 for Nav1.2 E1880K, and 6 for Nav1.3 K1826E. E, the voltage dependence of inactivation for Nav1.3 K1826D (triangles), Nav1.3 K1826A (squares), Nav1.3 K1826R (diamonds), and wild-type Nav1.3 (white circles) is shown. F, the voltage dependence of inactivation for Nav1.2 E1881D (triangles), Nav1.2 E1880K/E1881D (squares), and wild-type Nav1.2 (black circles) is shown. The parameters of the fits and sample sizes are shown in Table 3. Data points indicate means, and error bars show S.D. values.