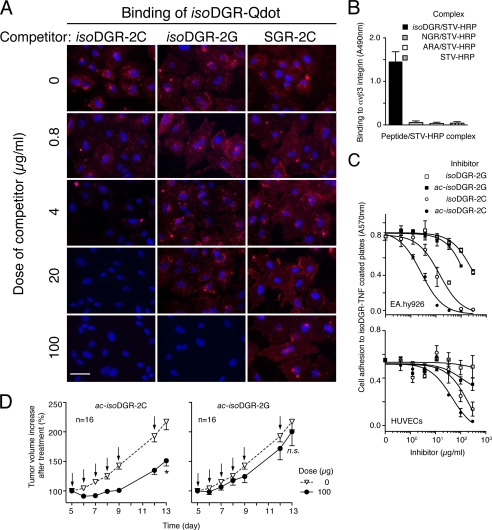
FIGURE 3.
Functional properties of different isoDGR peptides: αvβ3 integrin binding, inhibition of endothelial cell adhesion, and inhibition of tumor growth. A, competitive binding of isoDGR-Qdot with various doses of isoDGR-2C, isoDGR-2G, or SGR-2C to HUVECs. Representative images of three independent experiments are shown. Fluorescence microscopy assays were carried out as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Magnification, ×400; scale bar, 50 μm; red, Qdot; blue, nuclear staining with DAPI. B, binding of NGR/STV-HRP, isoDGR/STV-HRP, and ARA/STV-HRP to αvβ3 integrin. Complexes were diluted 1:500 in 25 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, containing 150 mm sodium chloride, 1 mm magnesium chloride, 1 mm manganese chloride, 3% BSA (1:500), added to microtiter plates coated with αvβ3, and incubated for 2 h at room temperature. After washing, the binding was detected by chromogenic reaction with 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine chromogenic substrate. Mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments (each in duplicate). C, inhibition of EA.hy926 cells adhesion (upper panel) or HUVECs adhesion (lower panel) to isoDGR-TNF-coated plates by acetylated (ac) and non-acetylated isoDGR-2C and isoDGR-2G peptides. Cell adhesion assay was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The representative results of three independent experiments (each in duplicate) is shown. D, anti-tumor effect of repeated administrations of ac-isoDGR-2C or ac-isoDGR-2G peptide (5 mg/kg, intraperitoneal) to WEHI-164 tumor-bearing mice. Animals were treated at the indicated times (arrows). Cumulative data of three independent experiments (16 mice/group in total) (mean ± S.E.) are shown. Two-tailed t test at day 13: *, p < 0.0003; n.s., not significant.