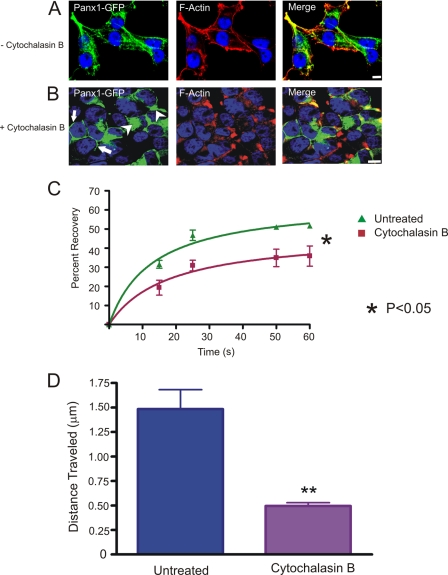
FIGURE 8.
Effect of cytochalasin B on Panx1-GFP. Untreated (A) or cytochalasin B-treated (B) Panx1-GFP-expressing BICR-M1Rk cells were labeled with phalloidin for F-actin localization. As expected, cytochalasin B caused the redistribution of F-actin from the cell surface (A) to the paranuclear region (B). The collapse of F-actin microfilaments coincided with the intracellular accumulation of Panx1-GFP (B, arrowheads), whereas a small population of Panx1-GFP remained evident at the cell surface (B, arrows). FRAP analysis in the presence of cytochalasin B treatment revealed that the cell surface population of Panx1-GFP was significantly impaired from entering the photobleached area (p < 0.05) (C) n = 3. Quantification of the total distance traveled by Panx1-GFP carrying vesicles within the same field of cells analyzed before and after the cytochalasin B treatment indicated a significant (p < 0.05) reduction in vesicle mobility in cytochalasin B-treated cells (D). Bars, 10 μm. Results shown are representative of five independent experiments.