Figure 1.
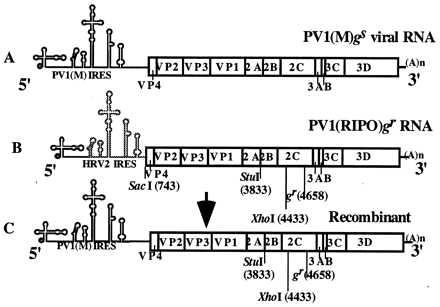
Schematic representation of the genotypes of parental RNA molecules and the resulting recombinant. (A) Genome of Gua-HCl-sensitive wild-type PV1(M)gs. The sphere at the 5′ end represents the genome-linked protein (VPg) that is attached to a clover leaf-like structure. Five stem-loop structures that follow form the IRES for PV (solid line) or HRV2 (broken line). The open box is the PV ORF encoding the polyprotein whose major cleavage products are indicated. The genome is terminated by 72 nontranslated nucleotides plus a poly(A) tail. (B) Genome of PV1(RIPO)gr, a chimera between PV and HRV2 that, in addition, contains two point mutations at nucleotide 4658/59 (Asn to Gly) leading to resistance (gr) against 2 mM Gua-HCl. Important restriction sites present only in the cDNA of PV1(RIPO)gr RNA (18) are shown. (C) The recombinant molecule that may have originated through crossover during minus-strand synthesis of PV1(RIPO)gr RNA in a region between the SacI and StuI restriction sites.
