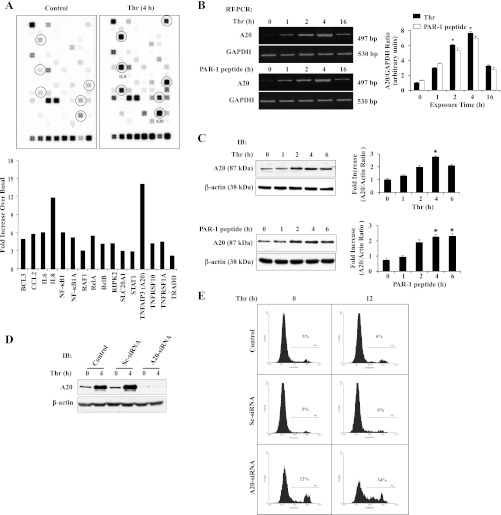
Fig. 2.
Protease-activated receptor (PAR)-1 signaling-induced A20 expression prevents apoptosis in ECs. A: ECs grown to confluence were challenged with thrombin (50 nM) for 4 h. After thrombin treatment, total RNA isolated was used for microarray analysis. The experiment was repeated twice with duplicates. Results from representative experiments are shown (top). The gene induction fold increase was calculated over basal with housekeeping gene GAPDH expression levels (bottom). B: ECs were treated with or without thrombin (50 nM) or PAR-1 agonist peptide (40 μM) for various time intervals. Total RNA was isolated and RT-PCR was performed to determine A20 and GAPDH expressions. The experiment was repeated 4 times, and results from a representative experiment are shown (left). RT-PCR gel images were quantified, and A20 mRNA induction fold increase over basal was calculated by measuring the ratio of A20 to GAPDH (right). *P < 0.05, significantly different from control. C: after thrombin (50 nM) or PAR-1 agonist peptide (40 μM) treatment, cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-A20 MAb. The membrane was stripped and reprobed with anti-β-actin Ab. The experiment was repeated 4 times, and results from representative experiment are shown (left). Immunoblots were quantified by densitometry, and A20 protein induction fold increase over basal was calculated by measuring the ratio of A20 to β-actin (right). *P < 0.05, significantly different from control. D: ECs were transfected with either 100 nM Sc-siRNA or A20-siRNA. At 48 h after transfection cells were immunoblotted with anti-A20 MAb. E: ECs were transfected with either 100 nM Sc-siRNA or A20-siRNA as described above. At 48 h after transfection, cells were treated with or without thrombin (50 nM) for 0 and 12 h. After thrombin treatment, cells were used for FACS analysis to determine apoptosis. The experiment was repeated 3 times, and results shown are from a representative experiment.