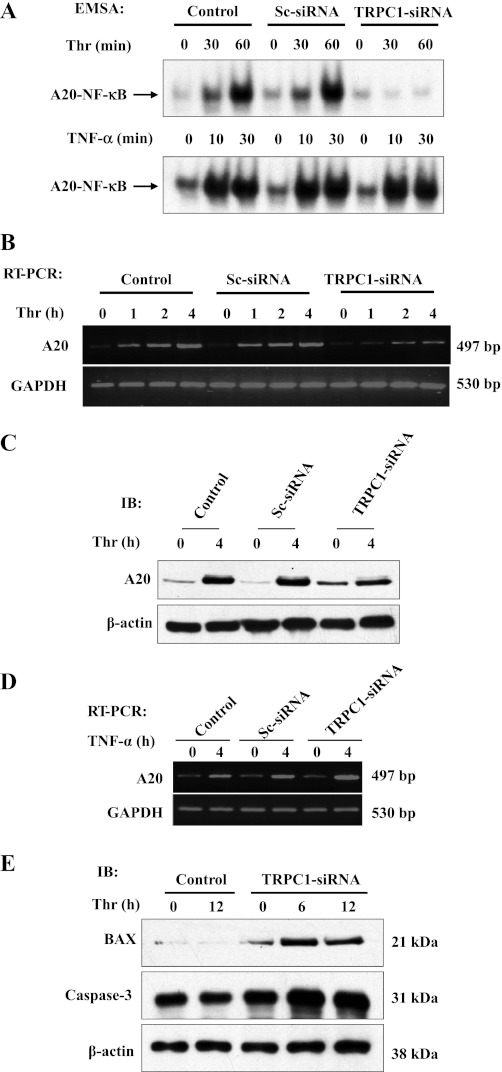
Fig. 4.
TRPC1 expression is required for thrombin-induced A20 expression in ECs. A: control ECs and ECs transfected with 100 nM Sc-siRNA or TRPC1-siRNA were exposed to thrombin (50 nM) or TNF-α (100 U) for the indicated time periods. After this treatment, EMSA was performed with A20 promoter-specific NF-κB probe as shown in Fig. 3B. The experiment was repeated 3 times with similar results, and results from representative experiments are shown. B: ECs were transfected with either 100 nM Sc-siRNA or TRPC1-siRNA. At 48 h after transfection, cells were exposed to thrombin (50 nM) for the indicated time periods. Total RNA was isolated, and RT-PCR was performed to determine A20 and GAPDH transcript expression levels. The experiment was repeated 3 times, and results from representative experiments are shown. C: control ECs and ECs transfected with 100 nM Sc-siRNA or TRPC1 siRNA were exposed to thrombin as described above. After thrombin exposure, cells were lysed and immunoblotted with anti-A20 MAb (top). The membrane was stripped and probed with β-actin Ab (bottom). D: control ECs and ECs transfected with 100 nM Sc-siRNA or TRPC1-siRNA were exposed to TNF-α (100 U) for 0 and 4 h. After TNF-α exposure, cells were used to measure A20 mRNA expression by RT-PCR. The experiment was repeated 3 times, and results from representative experiments are shown. E: control ECs and ECs transfected with TRPC1 siRNA as described above were treated with thrombin (50 nM) for 0, 6, and 12 h. After thrombin treatment, cells were lysed and immunoblotted with anti-BAX and anti-caspase-3 antibodies. The experiment was repeated 3 times, and results from representative experiments are shown.