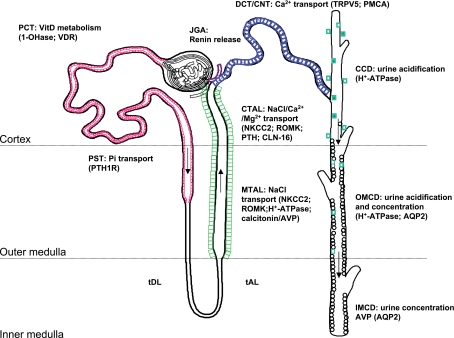
Fig. 1.
Intrarenal localization and roles of the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Cellular polarity of the CaSR is apical [in the proximal tubule and outer/inner medullary collecting duct (OMCD/IMCD)] and basolateral [in the thick ascending limb (TAL) and, occasionally, in the cortical collecting duct (CCD)]. Species differences exist in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT)/connecting segment (CNT), where receptor expression can be detected apically and/or basolaterally/intracellularly. PCT/PST, proximal convoluted/straight tubule; tDL/tAL, thin discending/ascending limb; MTAL/CTAL, medullary/cortical thick ascending limb; JGA: juxtaglomerular apparatus; TRPV5, transient receptor potential vanilloid 5; PMCA, plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase; VitD, vitamin D; VDR, vitamin D receptor; NKCC2, Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter 2; ROMK, renal outer medullary potassium K+ channel; PTH, parathyroid hormone; AQP2, aquaporin 2.