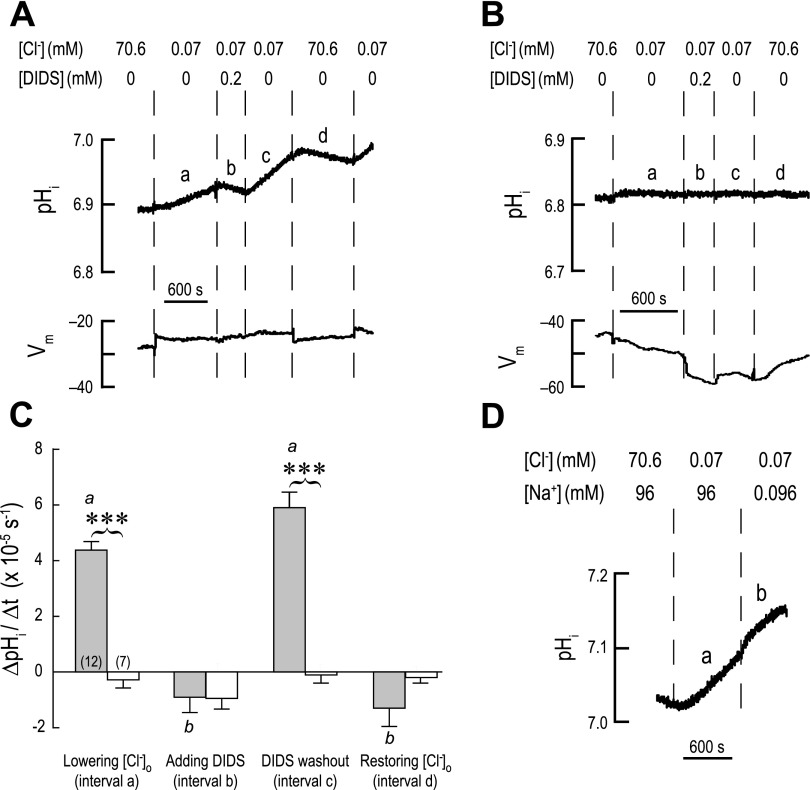
Fig. 12.
Cl− dependence, DIDS sensitivity, and Na+ independence of intracellular alkalinization in AeAE oocytes. A: representative recordings of pHi and membrane potential (Vm) in an AeAE oocyte exposed to a 5% CO2/33 mM HCO3− solution (solution III, Table 2) for 2 h prior. Extracellular concentrations (in mM) of Cl− and DIDS are indicated. When extracellular [Cl−] was lowered, it was replaced by gluconate. Solution changes are indicated by dashed vertical lines. Intervals a–d in the pHi trace indicate the intervals where rates of pHi change (ΔpHi/Δt) were measured. B: representative recordings of pHi and Vm in a H2O-injected oocyte, using a protocol similar to that described in A. C: summary of ΔpHi/Δt measurements. Shaded bars represent ΔpHi/Δt values of AeAE oocytes (number of oocytes shown in parentheses) during the intervals identified in A. The open bars represent H2O-injected oocytes at similar intervals. Values are means ± SE. Brackets connecting shaded and open bars represent comparisons in unpaired t-tests resulting in significant differences (***P < 0.001). a,bP < 0.001, categorization of the means of the AeAE oocytes as determined by a repeated-measures ANOVA and Newman-Keuls posttest. D: representative recording of pHi in an AeAE oocyte that examines the Na+ dependence of AeAE transport. Extracellular concentrations (in mM) of Cl− and Na+ are indicated. A total of 6 AeAE oocytes were evaluated using this protocol.