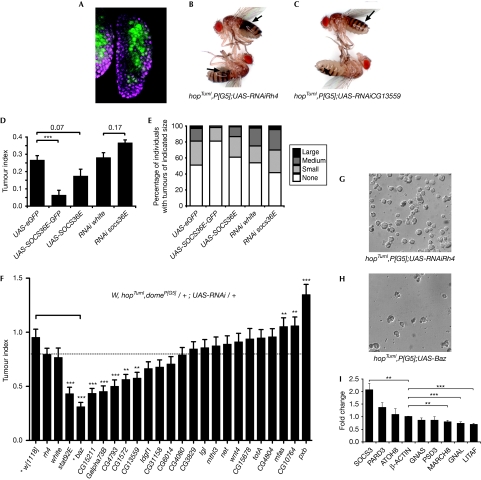
Figure 3.
In vivo characterization of JAK/STAT targets. (A) The third-instar lymph gland showing the domain of p[G5] expression (green) in the central MZ. DNA is shown in magenta. (B,C) Adult flies of the specified genotypes carrying the gain-of-function hopTumL allele contain multiple, large black tumours (indicated by arrows) when a control shRNA targeting rhodopsin 4 (rh4) is expressed in the MZ by the p[G5] driver (B). Flies in which the pathway effector CG13559 is knocked down contain fewer, smaller tumours (C). The TI (D) and percentage of adults with tumours of the indicated size (E) are shown for the specified genotypes, which either overexpress or knock down socs36E. Overexpression using UAS-SOCS36E-GFP flies showed significant reduction in TI as compared with that in the control (D). (F) The TI of flies of the indicated genotype expressing shRNAs targeting 21 potential effectors as well as rh4 and white as controls. The bar indicates the link between baz misexpression and w[1118] used as the control for this cross. (G,H) Representative differential interference contrast image of haemocytes from hopTumL larvae of the indicated genotypes showing reduction in circulating cells present after UAS-baz overexpression. (I) Fold change in the expression of selected homologues of Drosophila genes in HeLa cells after stimulation by the gain-of-function JAK2 V617F mutation. For all graphs, error bars represent standard error. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. baz, bazooka; GFP, green fluorescent protein; hop, Hopscotch; JAK, Janus kinase; MZ, medullary zone; shRNA, short-hairpin RNA; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TI, tumour index.