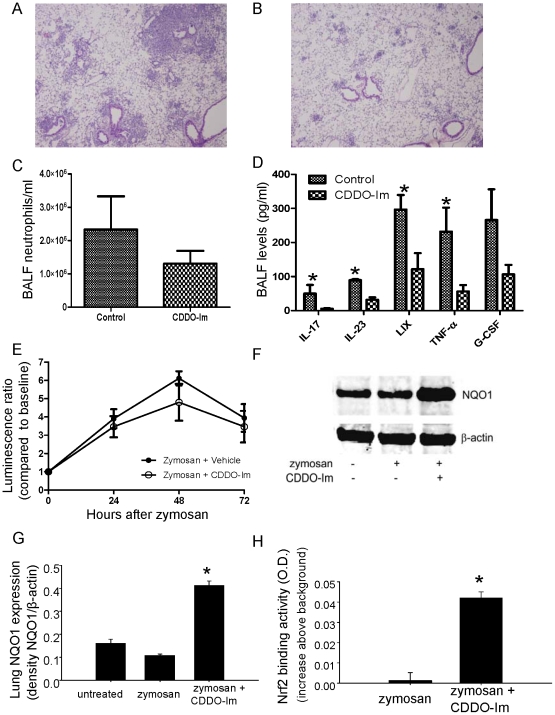
Figure 7. The triterpenoid, CDDO-Im, a Nrf2 inducer, reduces zymosan-induced lung inflammation and pro-inflammatory BALF cytokines in p47phox−/− mice.
CDDO-Im (0.2 mg/mouse by i.p. injection) or vehicle (control) was administered daily to p47phox−/− mice from day −1 to +2 in relation to i.t. zymosan, and BALF and lungs were harvested on day +3. Representative H&E stained lung sections of p47phox−/− mice administered zymosan plus vehicle (A) or zymosan plus CDDO-Im (B). Neutrophil (C) and cytokine (D) concentrations were assessed in BALF obtained at day 3 after zymosan treatment. Significant differences were observed for neutrophils (p = 0.03), IL-23 (p = 0.008), IL-17 (p = 0.02), TNF-α (p = 0.02), and LIX (p = 0.03) (Mann-Whitney two-tailed test). E) Lung NF-κB activation, measured by bioluminescence, was similar in p47phox−/− /HLL mice administered zymosan plus CDDO-Im versus zymosan plus vehicle (Two-way ANOVA, p = NS). F) Representative Western blot of lung homogenates for NQO1 and (G) densitometry (normalized to β-actin) (G) for 3 mice per genotype per treatment (p<.05 by ANOVA using Tukey post-test). Untreated = no experimental manipulation; zymosan = i.t. zymosan plus i.p. vehicle; zymosan + CDDO-Im = i.t. zymosan plus i.p. CDDO-Im. H) Measurement of Nrf2 activity by TransAM™ ELISA from whole lung nuclear protein extracts from p47phox−/− mice treated with zymosan plus vehicle or zymosan plus CDDO-Im. Results are presented as increase over background O.D. measurement in lung nuclear protein samples from Nrf2−/− mice (p<.05 using unpaired t-test).