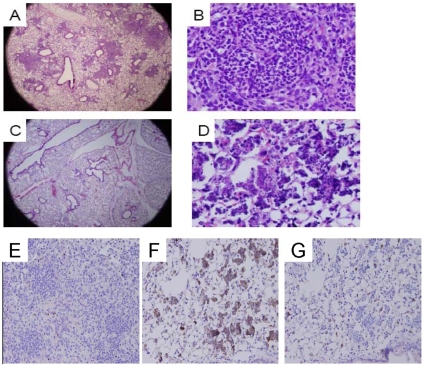
Figure 8. CDDO-Im reduces zymosan-induced lung inflammation in p47phox−/− mice in therapeutic studies by induction of apoptosis.
CDDO-Im (i.p. 0.2 mg/mouse) or vehicle was administered daily from days 2 to 5 and lungs were harvested on day 6 in relation to i.t. zymosan administration. A) Lung section of a p47phox−/− mouse administered zymosan and vehicle shows well-defined granulomatous lesions occupying approximately 40% of the lung (H&E, 20x). B) Higher magnification (400x) shows dense cellular granulomata composed of neutrophils and lymphohistiocytic infiltrates in mouse treated with zymosan and vehicle. C) In contrast, scant areas of inflammation were present in the lungs of p47phox−/− mice administered zymosan and CDDO-Im (H&E, 20x). D) At higher magnification (400x), small foci of degraded inflammatory cells were observed in CDDO-Im treated p47phox−/− mice. E–G) Cleaved caspase-3 immunostaining was augmented in lungs of p47phox−/− mice administered zymosan and CDDO-Im compared to zymosan and vehicle. E) Lung section of zymosan and vehicle-treated mouse shows dense inflammatory lesions with occasional apoptosis (H&E, 200x). F) Lung section of zymosan and CDDO-Im-treated mouse shows sparse areas of inflammation composed of apoptotic cells that are positive (brown staining) for cleaved caspase-3 (H&E, 200x). G) Same section as B with rabbit isotype shows background staining within alveolar epithelial cells, but not in areas of inflammation (H&E, 200x). Addition of blocking peptide eliminated anti-cleaved caspase-3 staining with the exception of background activity, confirming specificity of staining (data not shown). Sections are representative of 4 p47phox−/− mice per treatment group.