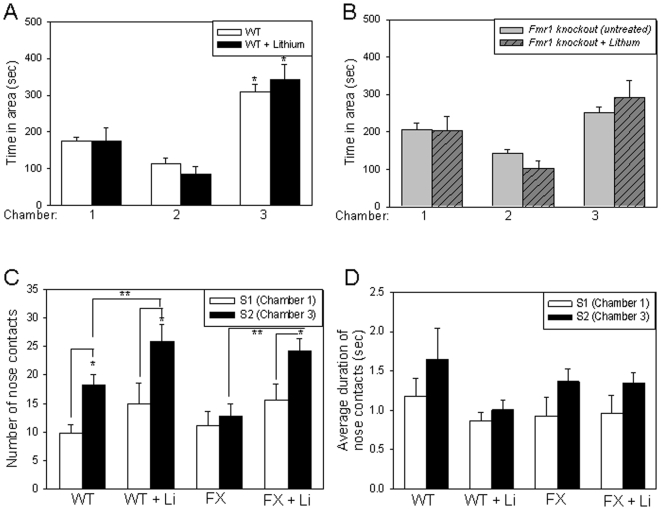
Figure 2. Fmr1 knockout mice exhibit impairments in social preference.
A. Mean total time spent by wild-type mice in each chamber during the social preference period. Wild-type (WT) mice (n = 9) spent significantly more time in Chamber 3 with the novel S2 mouse compared to empty Chamber 2, or to Chamber 1 with the familiar S1 mouse. Chronic lithium treatment did not significantly alter time spent in each chamber (n = 5). * p<0.05 comparing time spent in Chamber 3 with Chambers 1 and 2. B. Mean total time spent by Fmr1 knockout mice in each chamber during the social preference period. There was not a significant difference in the amount of time Fmr1 knockout (FX) mice (n = 9) spent in Chamber 3 with the novel mouse S2 and in Chamber 1 with the familiar mouse S1. Chronic lithium treatment did not significantly alter time spent in each chamber (n = 6). C. WT mice, but not FX mice, displayed a significant preference for nose contacts with S2, compared to S1. Chronic lithium treatment significantly increased the number of nose contacts with S2 by both WT and FX mice. * p<0.05 nose contacts with S2 compared with S1; ** p<0.05 compared to nose contacts with S2 by untreated group mates. D. The duration of nose contacts with S1 and S2 was not significantly different between WT and FX mice. Chronic lithium treatment had no significant effect on nose contact duration.