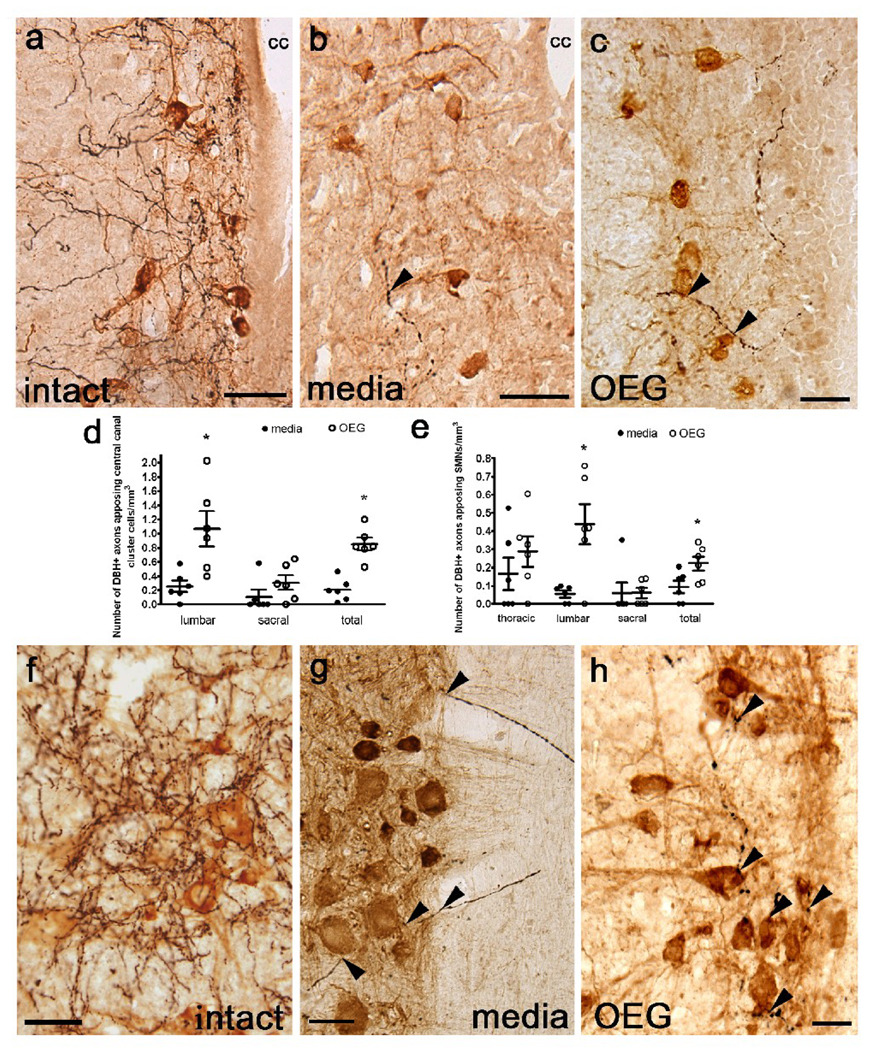
Fig. 5.
Noradrenergic (NA) axons labeled with dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH) appose central canal cluster cells (a–c) and somatic motor neurons (f–h) in the lumbar spinal cord from intact, media-, and OEG-injected spinal rats. (a–c) Many DBH-positive fibers (black) course near central canal cluster cells (brown) in a sagittal section from an intact rat (a) with fewer fibers found in spinal rats (b, c; arrowheads). cc = central canal (d) OEG-injected rats contain significantly more appositions of DBH-positive fibers along central canal cluster cells than media-injected rats at lower lumbar (P = 0.006) but not at sacral (P = 0.09) levels. When data from both segments were combined, OEG-injected rats contained more DBH-positive varicosities apposing central canal cluster cells than media-injected rats (P = 0.003) (e) The number of DBH-labeled fibers apposing SMNs at the lumbar level was greater in OEG- than media-injected rats (P = 0.014). When data from all segmental levels were combined, OEG-injected rats contained more DBH-positive varicosities apposing SMNs than media-injected rats (P = 0.017). (f–h) Numerous NA axons appose SMNs in an intact rat (f). DBH-positive axons (arrowheads) associate with blood vessels that course within the white matter and then appose SMNs (brown) in a media-injected rat (g). Varicose NA axons are associated with SMNs in an OEG-injected spinal rat (h). Bars in (d, e) indicate mean ± SEM for 6 media-injected and 6 OEG-injected rats. *significant difference between media- and OEG-injected rats. Scale a–b, f–h = 50 µm, Scale c = 25 µm.