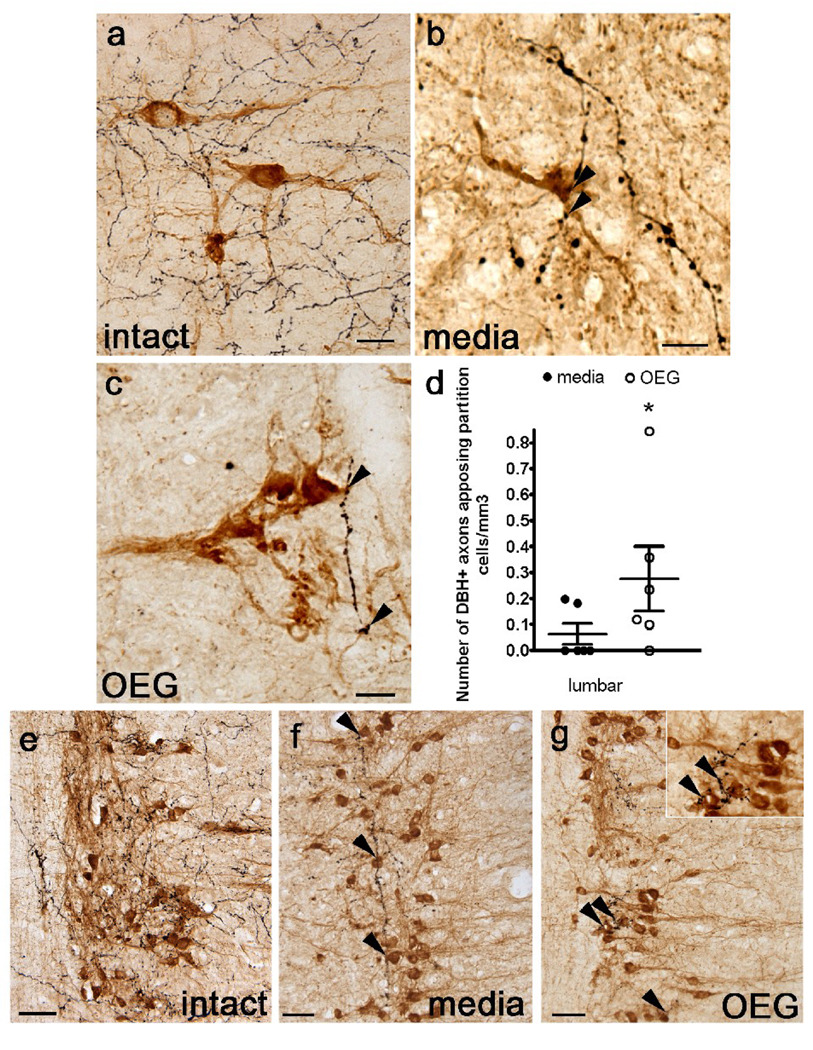
Fig. 6.
Dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH)-labeled axons appose cholinergic partition cells in sagittally sectioned lower lumbar spinal cord and parasympathetic preganglionic neurons (PPNs) in the sacral cord of an intact rat, and in media- and OEG-injected spinal rats. (a–c) Many DBH-labeled axons (black) course near partition cells (amber-brown) in intact rats (a). DBH-positive axons (arrowheads) also course near partition cells in the caudal stump of media- (b) and OEG-injected (c) spinal rats. (d) The density of DBH-labeled axons that appose partition cells in the lumbar spinal cord is significantly higher in OEG- than media-injected rats (P = 0.004). (e–g) DBH-labeled axons, presumably from the locus coeruleus, densely innervate cholinergic PPNs (brown) in intact rats (e). DBH-positive axons (arrowheads) course among clusters of PPN in media- (f) and OEG-injected (g) spinal rats. Area in (g) marked by double arrowhead is enlarged (inset) to illustrate the proximity of DBH-labeled axons to PPNs. Bars in (d), mean ± SEM for 6 media- and 6 OEG-injected rats. *significant difference between media- and OEG-injected rats. Scale a–c, e–f = 50 µm.