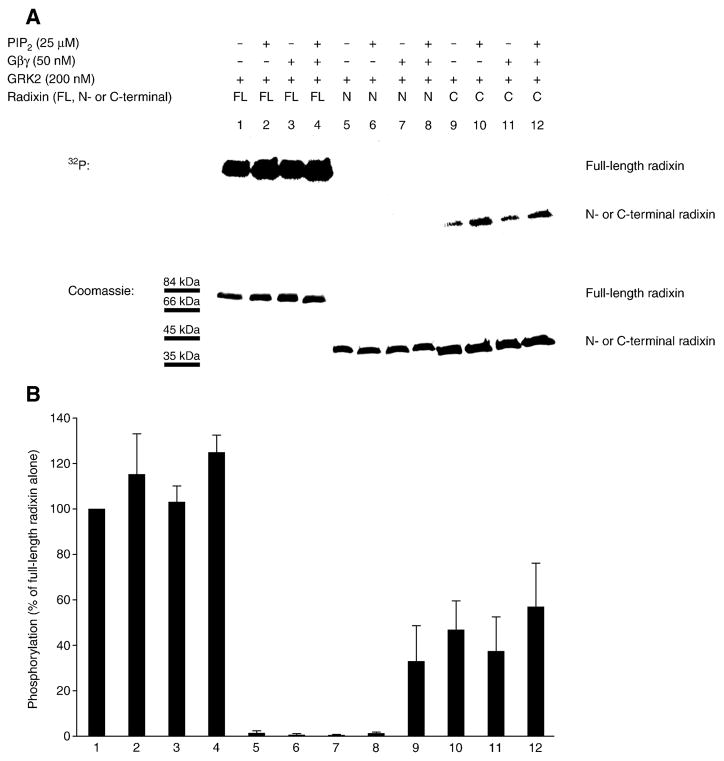
Figure 4. GRK2 phosphorylates the C-terminal region of radixin in vitro.
(A) Kinase assays were performed with purified recombinant GRK2 and recombinant full-length radixin (FL; lanes 1, 2, 3 and 4), N-terminal radixin fragment (N-term; lanes 5, 6, 7 and 8) and C-terminal radixin fragment (C-term; lanes 9, 10, 11 and 12), in the absence (lanes 1, 5 and 9) or presence of PIP2 (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12) or Gβγ subunits (lanes 3, 4, 7, 8, 11 and 12). [γ-32P]-ATP-labeled protein is shown in the autoradiogram at the top, while total Coomassie blue-stained protein is shown for equivalent loadings at the bottom. (B) Levels (mean and SEM) of [γ-32P]-ATP-labeled protein quantitated from autoradiograms from four independent experiments as in A are shown, with values expressed as a percent of the level of phosphorylation of full-length radixin alone (without PIP2 or Gβγ subunits) by GRK2 (normalization to the parallel full-length radixin result for each experiment prior to statistics).