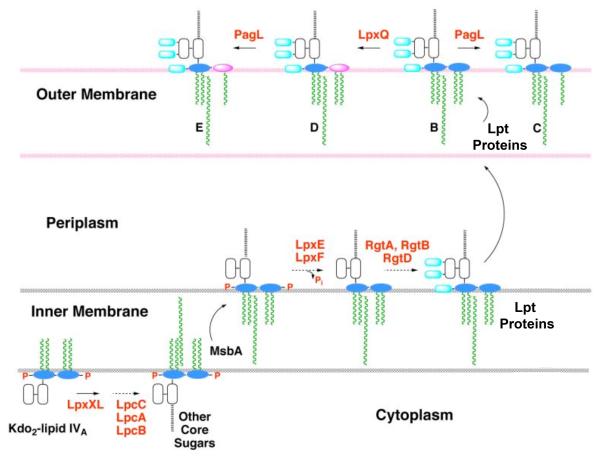
Figure 2. Topography of LPS assembly and lipid A modification in R. etli.
With the exception of the UDP-diacylglucosamine hydrolase LpxH, which is replaced by LpxI (L. E. Metzler and C. R. H. Raetz, in preparation), the constitutive enzymes that generate the phosphorylated intermediate Kdo2-lipid IVA in E. coli are also present in R. etli [17]. The assembly of R. etli lipid A diverges after Kdo2-lipid IVA formation, starting with the addition of the 27-hydroxyoctacosanoate chain (27OHC28:0), catalyzed by LpxXL [20]. After completion of core glycosylation and transport to the outer surface of the inner membrane by MsbA, LpxF and LpxE remove the phosphate moieties at the 4′- and 1-positions, respectively [22, 23, 25]. Next, RgtD is thought to utilize dodecaprenyl phosphate-galacturonic acid to incorporate the 4′-galacturonic acid residue, and RgtA/RbtB similarly modify the outer Kdo unit [26, 27]. After completion of O-antigen assembly (not shown) and transport to the outer membrane by the Lpt proteins [68], the ester-linked hydroxyacyl chain at position 3 may be removed by the deacylase PagL [30, 31], and the proximal glucosamine may be converted to the aminogluconate unit by the oxidase LpxQ [28, 29]. The orientation of the LpxQ active site within the outer membrane is not established unequivocally.