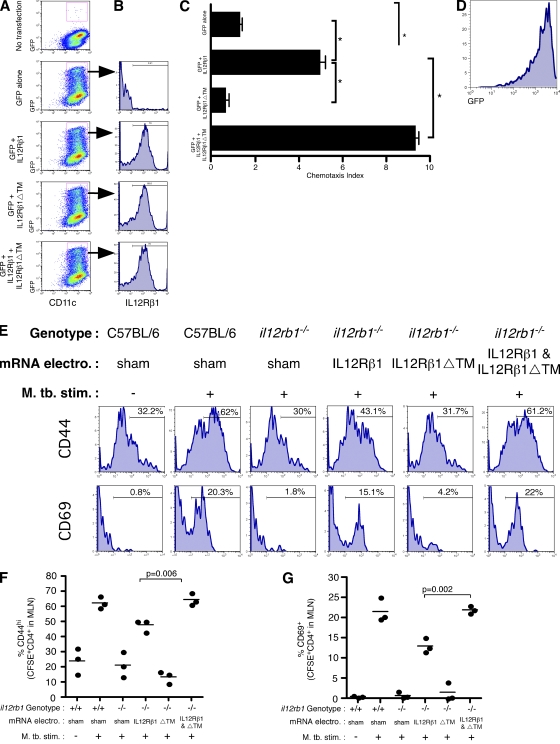
Figure 8.
IL-12Rβ1ΔTM enhances IL-12Rβ1-dependent migration. (A–D) il12rb1−/− CD11c+ BMDCs were transfected with mRNAs encoding either GFP, GFP and IL-12Rβ1, GFP and IL-12Rβ1ΔTM, or GFP and IL-12Rβ1 and IL-12Rβ1ΔTM. 24 h later, (A) cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for GFP expression among CD11c+ cells and (B) expression of transfected IL-12Rβ1 was examined by gating on GFP+CD11c+ cells. (C) The migratory ability of DCs transfected with the indicated mRNAs was assessed as performed in Fig. 1 C. Data points represent the mean and SD of the combined data from three separate experiments with different BM preparations per experiment. For the difference between CI induced in the indicated groups, *, P < 0.05, as determined by Student‘s t test. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of those cells that had migrated and transfected with GFP and IL-12Rβ1 and IL-12Rβ1ΔTM demonstrates that the migratory DCs from this group were mostly GFP+. (E) We compared the ability of il12rb1−/− DCs transfected with indicated mRNAs to activate M. tuberculosis-specific T cells in vivo; sham-transfected C57BL/6 DCs were used as a positive control. After transfection the indicated DCs populations were cultured with M. tuberculosis and ESAT1-20 peptide; after this they were instilled via the trachea into C57BL/6 mice containing transferred CFSE-labeled ESAT-specific CD4+ cells. Shown are histograms of CD44 and CD69 expression on CFSE+CD4+ 12 h later in the draining MLN. Each histogram is representative of four mice per condition. (F and G) The combined (F) CD44 and (G) CD69 data gated on CFSE+CD4+ in the draining MLN are shown; these data are representative of two independent experiments with three to four mice per group.