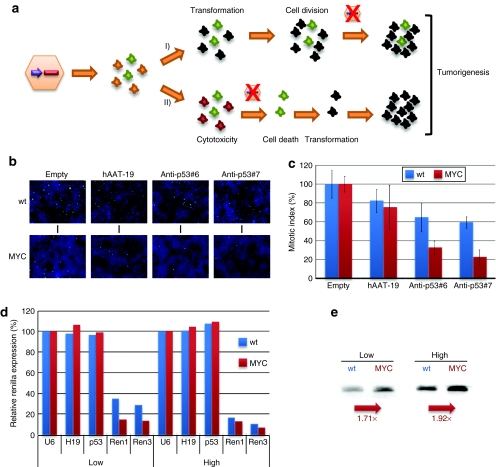
Figure 7.
Identification of intracellular MYC–shRNA interactions. (a) Two alternative models for MYC–shRNA interactions in cells/tissues (scheme). In model 1, shRNAs enhance MYC's ability to transform cells, resulting in proliferation and loss of AAV vector genomes. In model 2, MYC increases shRNA activity and thus cytotoxicity, causing local cell death (and thus AAV loss) and transformation/proliferation of adjacent cells. (b) PH3 staining to determine mitotic indexes under various combinations of MYC and shRNA expression (mean ± SD from three independent experiments in c). Mitotic indexes were normalized to cells transfected with an empty U6 vector. (d) Renilla luciferase knockdown with specific shRNAs in the presence or absence of MYC (means from two independent experiments). The shRNAs were transfected at two different doses (low/high = 10/100 µg per well in 24-well plates). (e) MYC increases shRNA expression from U6 promoters (northern blot analyses, numbers indicate representative values). AAV, adeno-associated virus; hAAT, human α-1-antitrypsin; shRNA, short hairpin RNA.