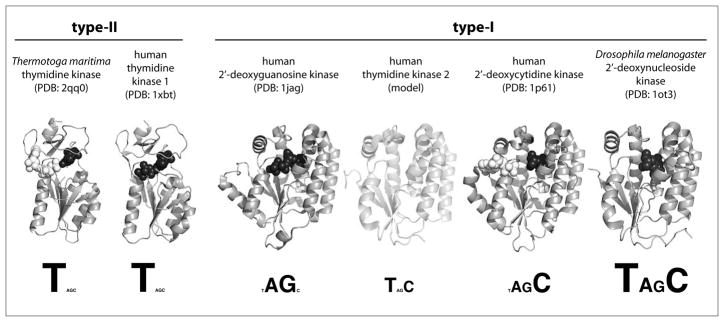
Fig. 3.
Summary of structure and substrate specificity of the 2′-deoxynucleoside kinase family. Members are divided into type-I and type-II subfamilies based on their distinct structural features. Representative protein structures, shown as grey ribbons, are based on crystal structure coordinates except for the homology-based model of human TK2. Where available, substrate occupying the phosphoryl-acceptor binding site is shown as black spheres while substrate binding in the phosphoryl-donor site is marked by white spheres. Substrate profiles are displayed beneath the structures, reflecting each enzyme’s catalytic efficiency for the four natural 2′-deoxynucleosides (T, dA, dG, dC) by their font sizes.