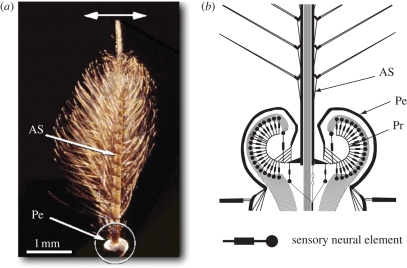
Figure 1.
Morphology of the antennal hearing organ of the mosquito Toxorhynchites brevipalpis. (a) The male antennal shaft (AS) is approximately 3.5 mm long and bears numerous fine hairs. At the base of the shaft, the pedicel (Pe) contains Johnston's organ, where mechanosensory neurons receive sound-induced vibrations. The main mode of vibration of the antenna is an oscillation (horizontal arrow). (b) Schematic cross-section of the mosquito pedicel (enlarged circled area in a) highlighting the structure of Johnston's organ, the site of the mechanosensory neuronal elements. Oscillations of the antennal shaft are transmitted to the mechanosensory neurons through curved prongs (Pr) connected to the base of the shaft.