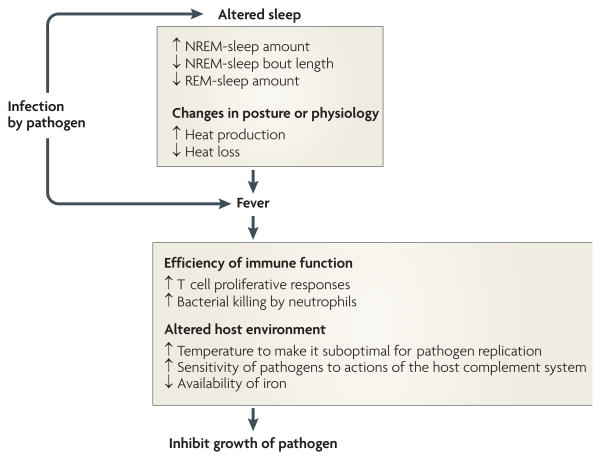
Figure 4. Proposed principles by which changes in sleep architecture promote recovery from infection.
Infection-induced alterations in sleep are such that increases in non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep provide energy savings, and short NREM-sleep bouts reduce heat loss. The reduction in REM sleep allows the animal to shiver. The combined changes in NREM and REM sleep facilitate the production of fever. Fever imparts survival value because it increases the efficiency of many facets of immune function and alters the host environment to make it less favourable for pathogen reproduction97.