Fig. 5.
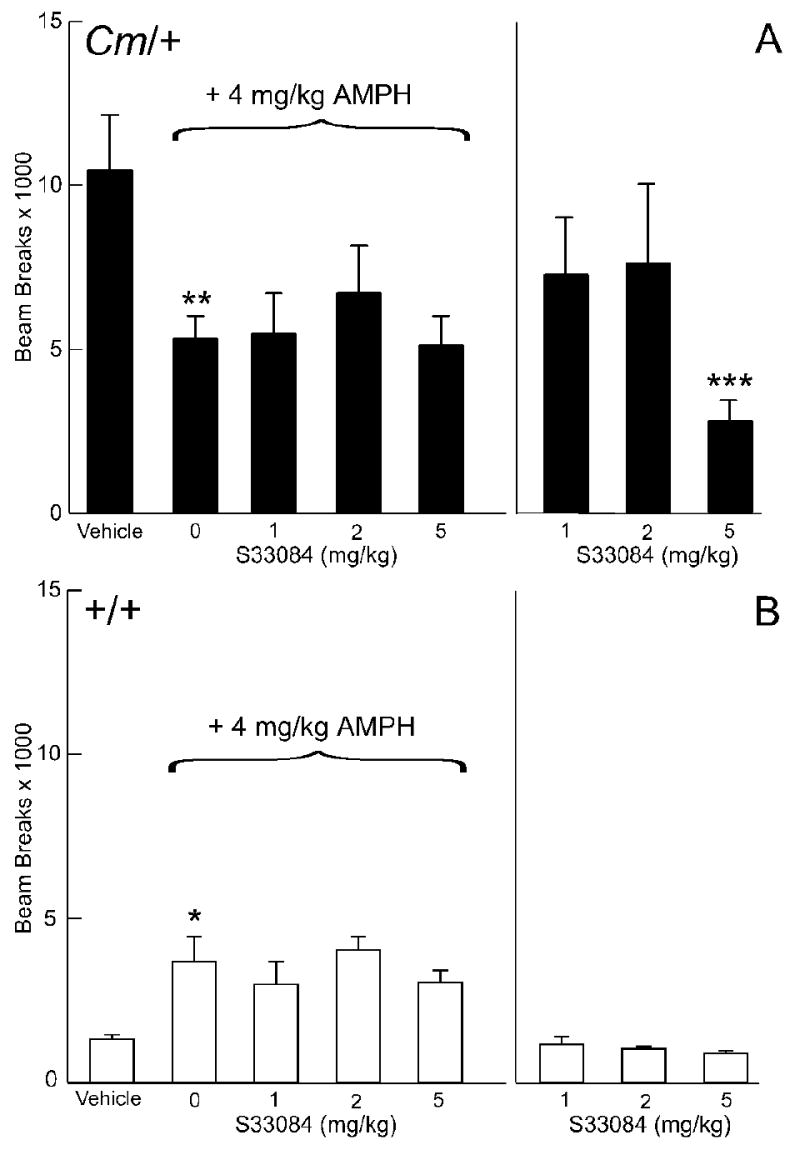
Effect of the D3-selective dopamine receptor antagonist S33084 on amphetamine-mediated locomotor activity. Coloboma (A) and control mice (B) were treated with saline or 4 mg/kg amphetamine and challenged with S33084. Compared to vehicle treatment, amphetamine significantly increased locomotor activity in control mice (*p < 0.05) but significantly reduced locomotor activity in coloboma mice (**p<0.01). There was a significant effect of genotype (F1,14 = 11.2, p < 0.01) without significant effect of dose or genotype × dose interactions. Treatment with S33084 alone produced a significant genotype × dose interaction effect (F3,42 = 8.3, p < 0.001). Compared to vehicle treatment, 5 mg/kg S33084 significantly reduced locomotor activity in coloboma mice (***p < 0.001); the locomotor activity of control mice was unaffected by any dose. Data are beam breaks accumulated in 1 hr following drug treatment and are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 8/genotype/dose).
