Figure 2.
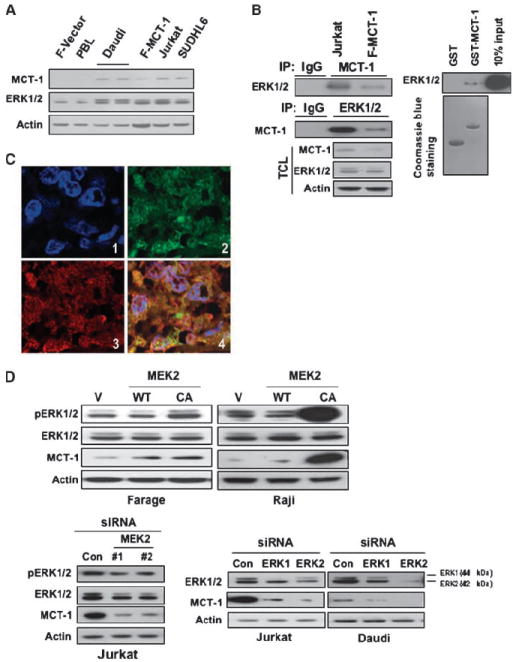
ERK positively modulates levels of MCT-1 protein. A, cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. B, MCT-1 associates with ERK in cells. Left, Jurkat and Farage–MCT-1 cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) using either anti–MCT-1 or anti-ERK1/2 antibody, followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. TCL, total cell lysate. Right, MCT-1 associates with ERK in vitro. GST-fused MCT-1 was immobilized onto GS beads and then incubated with Jurkat cell lysates. Immunoblotting was followed using anti-ERK1/2 antibody. C, colocalization between MCT-1 and ERK in human lymphoma tissues. Double immunofluorescent staining for MCT-1 (green) and ERK (red) at ×600 magnification indicates that there is strong overlapping in human lymphoma tissues. 1, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI); 2, MCT-1; 3, ERK; and 4, merged image of MCT-1, ERK, and DAPI. D, overexpression of constitutively active (CA) MEK2 increased MCT-1 protein level. Farage or Raji cells were transfected with WT MEK2, CA MEK2 construct, or the vector control (V). The cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis (top). Bottom, knocking down of MEK2 and ERK1/2 decreased MCT-1 expression. Jurkat or Daudi cells were transfected with control siRNA or siRNAs specific for MEK2, ERK1, and ERK2. At 72 h after transfection, the expression of pERK1/2, ERK1/2, or MCT-1 was monitored by immunoblotting.
