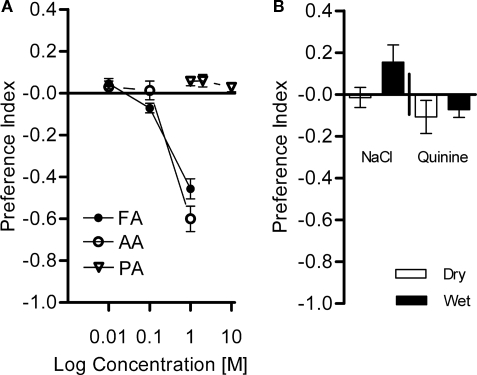
Figure 9.
Avoidance of diverse chemical substances. Choices between different chemical solutions and the control (water) were given to naïve flies. (A) Acid avoidance. Flies were tested with formic acid (FA), acetic acid (AA) at 0.01–1 M, and phosphoric acid (PA) at 1–10 M. Strong avoidance was found for FA and AA at 1 M [one-sample t-test, AA 1 M: t(7) = 16.73, P < 0.001; FA 1 M: t(7) = 15.13, P < 0.001], whereas moderate avoidance, if at all, was observed at lower concentrations [one-sample t-test, AA 0.01 M: t(7) = 1.134, P > 0.05; AA 0.1 M: t(7) = 4.787, P < 0.05; FA 0.01 M: t(7) = 0.2669, P > 0.05; FA 0.1 M: t(7) = 1.358, P > 0.05]. PA did not evoke a significant avoidance at any of the tested concentrations [one-sample t-test, PA 1 M: t(7) = 1.356, P > 0.05; PA 2 M: t(7) = 0.2009, P > 0.05; PA 10 M: t(7) = 0.5641, P > 0.05]. n = 8. (B) Avoidance of NaCl (6 M) and quinine (0.1 M). Both substances were assayed with dry or wet filter paper. No avoidance of the flies to these substances at any condition was found [one-sample t-test, NaCl dry: t(9) = 0.3021, P > 0.05; NaCl wet: t(9) = 1.872, P > 0.05; quinine dry: t(9) = 1.353, P > 0.05; quinine wet: t(7) = 1.959, P > 0.05]. n = 10.