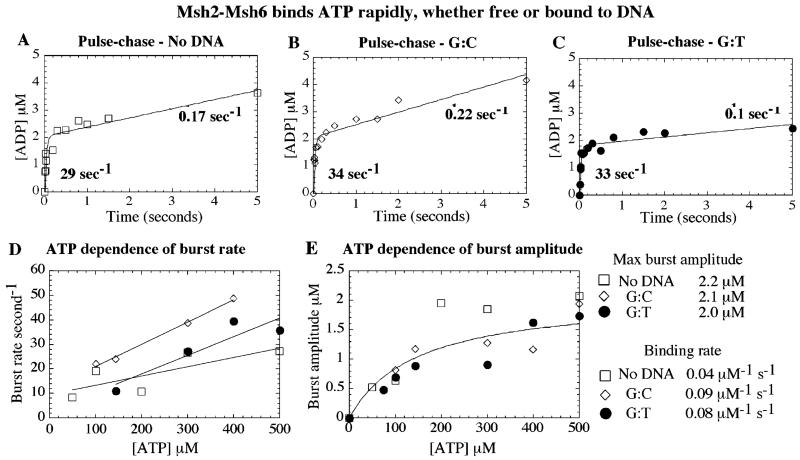
Figure 6.
Msh2-Msh6 binds ATP rapidly–free or in complex with DNA. Pre-steady-state pulse-chase assays were performed with 2 μM Msh2-Msh6 and 0–500 μM α32P-ATP, ± 3 μM DNA, and 5 mM unlabeled Mg2+-ATP chase (for 35 s after 0.01–5 s reaction times). Representative time courses with 500 μM ATP show that Msh2-Msh6 binds ATP rapidly, (A) in the absence of DNA and (B) in the presence of G:C or (C) G:T DNA. (D) ATP dependence of the burst rate yields a bimolecular ATP binding constant ~0.1 μM−1 s−1. (E) ATP dependence of the burst amplitude yields maximum 2 μM ATP hydrolyzed rapidly in one turnover (fit shown only for Msh2-Msh6·G:T DNA, for clarity).