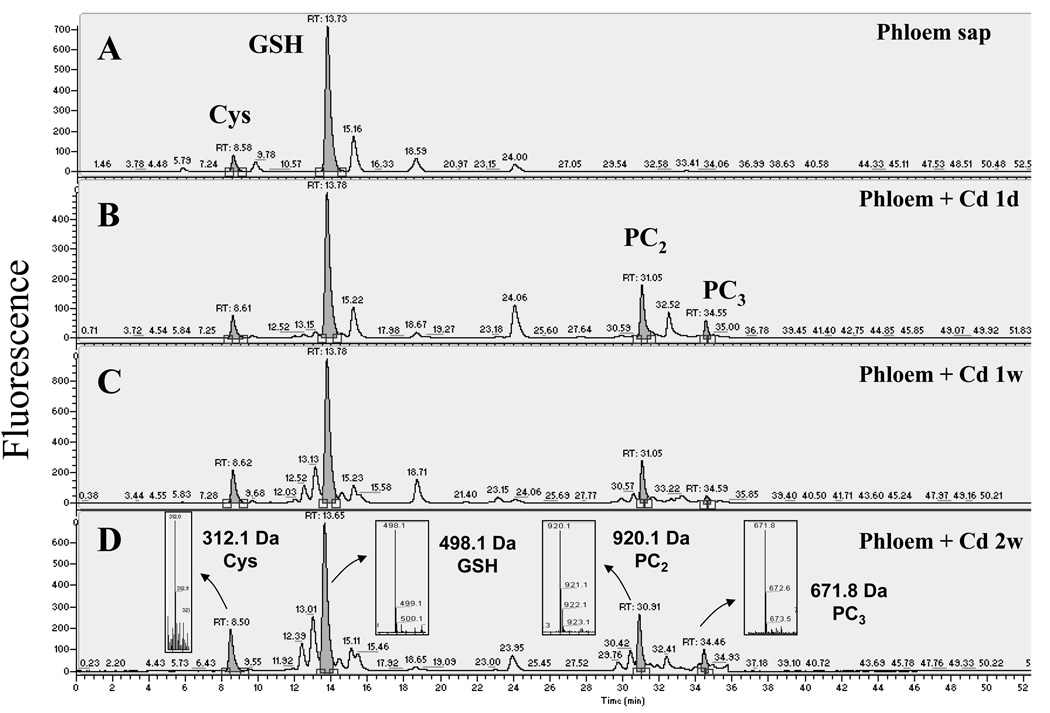
Figure 2.
Cadmium exposure results in the appearance of phytochelatins (PCs) in the phloem sap of Brassica napus. Thiols from (a) control and plants exposed to 75 µm CdSO4 for (b) 1 day, (c) 1 week and (d) 2 weeks were labeled with monobromobimane, separated by reverse phase HPLC and detected by fluorescence. Thiols were identified with a mass spectrometer coupled to the HPLC. Phytochelatins appeared after 1 day of cadmium exposure and their concentrations increased with the time of exposure. Note the difference in the Y-axis scales in panels (c) and (d). The insets in (d) show the mass spectrum of the corresponding monobromobimane-labeled thiols. Bimane label accounts for the addition of 190 Da per thiol to the mass of the unlabeled compounds.