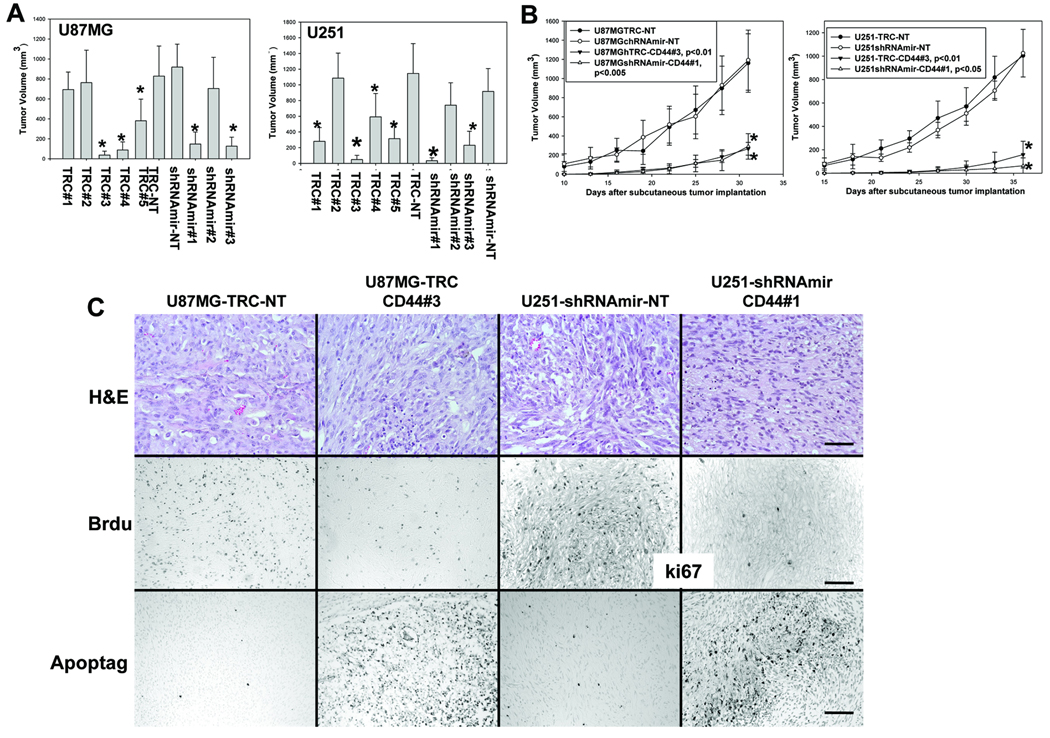
Figure 2. Knockdown of CD44 expression inhibits subcutaneous growth of U87MG and U251 glioma cells by inhibiting proliferation and promoting apoptosis of the cells in vivo.
5 ×106 glioma cells were injected subcutaneously per mouse. A, The effects of CD44 knockdown on subcutaneous growth of U87MG (left) and U251 (right) cells infected with different shRNA constructs were assessed by measuring tumor volume 5 weeks after tumor cell implantation. B, Growth rates of the subcutaneous tumors derived from U87MG (left) and U251 (right) cells infected with different shRNA constructs were determined and expressed as the mean of tumor volumes (mm3) +/− SD. Six mice were used for each type of transduced glioma cells in panel A and B. C, Morphology, proliferation and apoptosis status of subcutaneous gliomas were assessed. Tumor sections were stained with H&E for histology (C, top panels). In vivo glioma cell proliferation was detected using an anti-BrdU (Roche, C, middle, first two panels) and an anti-k67 antibody (C, middle, last two panels). Apoptotic GBM cells in situ were detected using Apoptag kit (Chemicon, C, bottom panels). Bar, in a-d, 50µm and in e-l, 100 µm.