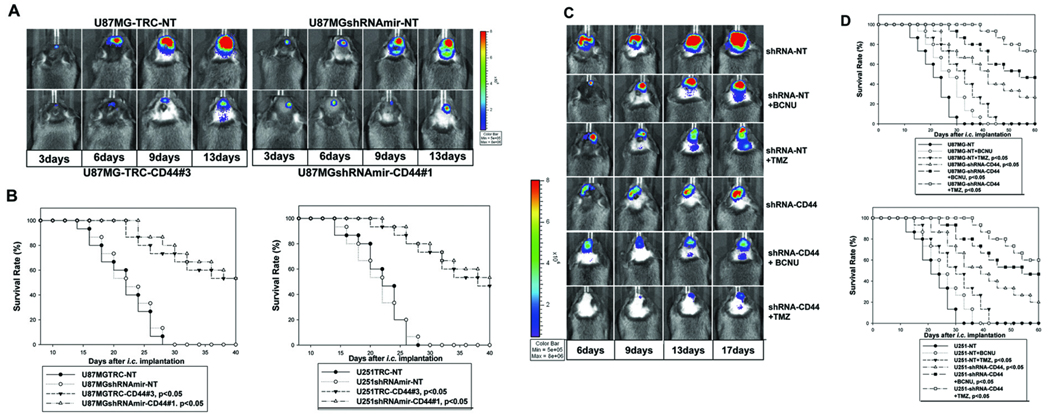
Figure 3. Knockdown of CD44 expression inhibits intracranial growth of U87MG and U251 gliomas and sensitizes responses of the glioma cells to cytotoxic drugs in vivo.
A, Bio-luminescence imaging analysis of mice 3, 6, 9, and 13 days following the intracranial injection of U87MG-TRC-NT, U87MGshRNAmir-NT controls (upper panels), and U87MG-TRC-CD44#3 and U87MGshRNAmir-CD44#1 (shRNAs effectively knock down CD44 expression, bottom panels). B, Survival rates of mice following intracranial injections of the transduced U87MG (B, left) and U251 (B, right) cells as detailed in the panels. 15 mice were used for each type of transduced GBM cells. C, Bioluminescence imaging analysis of mice 6, 9, 13, and 17 days following intracranial injection of U87MG-NT (shRNA controls), or U87MGshRNA-CD44 (a mixture of shRNAs effectively knocks down CD44 expression). Mice were injected with or without a single dose of BCNU (10 mg/kg) or TMZ (5mg/kg) 3 days after intracranial injection of the tumor cells. D, Survival rates of mice following intracranial injections of the transduced U87MG (top) and U251 (bottom) cells are shown in the panels. 15 mice were used for each treatment.