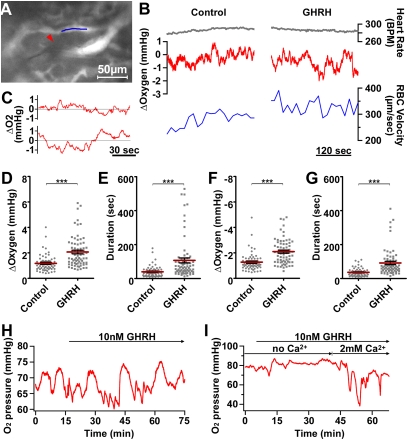
Fig. 4.
In situ Ptiss,O2 responses to GHRH. (A–G) In vivo measurements of pituitary Ptiss,O2 levels with oxygen microsensors in anesthetized GH-eGFP mice. (A) The tip (5 μm) of an oxygen sensor (red arrowhead) was inserted into a GH cell cluster (not illustrated). RBC velocity was monitored in a nearby capillary filled (indicated with a blue line segment) i.v. with rhodamine 70-kDa dextran. (B) In the same experiment, heart rate (top traces), relative changes in Ptiss,O2 levels (middle traces), and RBC velocity (bottom traces) were monitored before (Left) and after i.v. (Right) GHRH injection. (C) In another experiment, expanded time-lapse recordings of relative changes in Ptiss,O2 levels before (top trace) and after (bottom trace) i.v. GHRH injection. (D and E) Distributions of both amplitude (D) and duration (E) of upward Ptiss,O2 deflections measured before (control) and after (GHRH) secretagogue injection. (F and G) Distributions of both amplitude (F) and duration (G) of downward Ptiss,O2 deflections measured before (control) and after (GHRH) secretagogue injection. Represented are the means ± SEM for control and GHRH-stimulated conditions (***P < 0.001, n = 7 animals). (H and I) Monitoring of pituitary Ptiss,O2 levels with oxygen microsensors in acute GH-eGFP pituitary slices perfused with saline solution. (H) Large spontaneous downward Ptiss,O2 deflections occurred within a GH cell cluster. Subsequent bath application of GHRH at 10 nM (top horizontal arrow) induced larger and longer Ptiss,O2 deflections with superimposed smaller Ptiss,O2 deflections. (I) No large downward O2 changes occurred in a pituitary slice preincubated with a calcium-free saline solution (with 5 mM EGTA). Ten nanomolar GHRH triggered large downward O2 changes only when the calcium concentration was restored to 2 mM in the bathing medium.