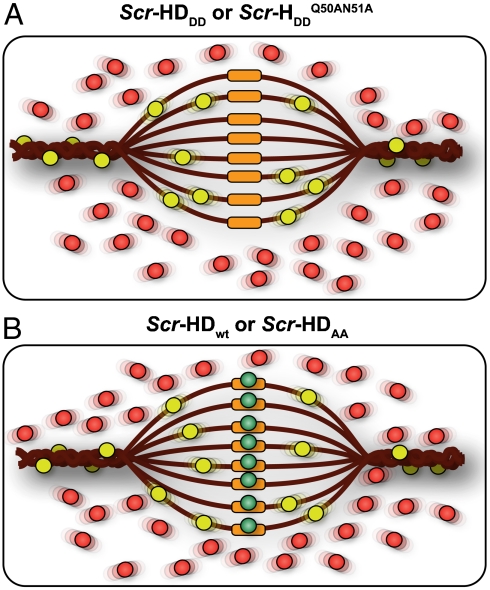
Fig. 6.
Schematic representation of the differential behavior of Scr-HD variants. (A) In nuclei expressing the transcriptionally inactive variants Scr-HDDD or 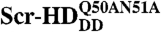 FCS can distinguish between free Scr-HD molecules diffusing in the nucleoplasm (Red Spheres) and transcription factor molecules interacting nonspecifically with the DNA (Yellow Spheres). Binding sites within the region of loose chromatin conformation (Orange Rectangles) cannot be bound specifically by Scr-HDDD or
FCS can distinguish between free Scr-HD molecules diffusing in the nucleoplasm (Red Spheres) and transcription factor molecules interacting nonspecifically with the DNA (Yellow Spheres). Binding sites within the region of loose chromatin conformation (Orange Rectangles) cannot be bound specifically by Scr-HDDD or 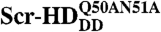 because binding is abolished by the corresponding amino acid substitutions. (B) DNA - Scr-HDwt or DNA - Scr-HDAA interactions are more complex. In addition to the free Scr-HD molecules in the nucleoplasm (Red Spheres) and transcription factor molecules interacting nonspecifically with the DNA (Yellow Spheres), the transcriptionally active variants undergo also specific interactions (Green Spheres) with putative specific binding sites.
because binding is abolished by the corresponding amino acid substitutions. (B) DNA - Scr-HDwt or DNA - Scr-HDAA interactions are more complex. In addition to the free Scr-HD molecules in the nucleoplasm (Red Spheres) and transcription factor molecules interacting nonspecifically with the DNA (Yellow Spheres), the transcriptionally active variants undergo also specific interactions (Green Spheres) with putative specific binding sites.