Fig. 2.
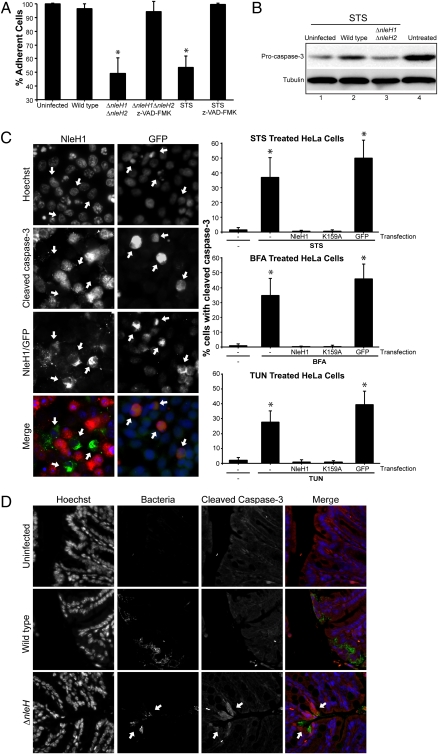
NleH inhibits caspase-3 activation. (A) Z-VAD-fmk inhibits EPEC-induced cell detachment. HeLa cells treated with the caspases inhibitor Z-VAD-fmk were infected with WT EPEC, ΔnleH1ΔnleH2 mutant, and p(nleH1)- or p(nleH2)-complemented strains, and the number of live adherent cells was counted. Z-VAD-fmk inhibited loss of STS-treated control and EPEC ΔnleH1ΔnleH2-infected cells. *P <.05. The nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to determine significance, because the data did not follow a Gaussian distribution. *P <.05. (B) Analysis of procaspase-3 cleavage. HeLa cell lysates, infected for 1 h with WT EPEC or ΔnleH1ΔnleH2 mutant and then treated for 3 h with STS, were analyzed by Western blot with procaspase-3 (inactive) and tubulin-control antibodies. Untreated uninfected lysates served as controls (lane 4). STS treatment induced capase-3 activation (lane 1). Infection with WT EPEC inhibited STS-induced procaspase-3 cleavage (lane 2), whereas infection with ΔnleH1ΔnleH2 mutant did not (lane 3). (C) Cleaved caspase-3 (active) was quantified in cells transfected with nleH1, nleHK159A, or pEGFP and treated with STS, BFA, or TUN. Anti-HA (green) and anti–cleaved caspase-3 (red) were used to detect HA-NleH1 and NleH1K159A or active caspase-3 by immunofluorescence. Ectopic expression of NleH1 or NleH1K159A prevented cleavage of procaspase-3 by treatment with STS (B), BFA (C), and TUN (D) compared with mock-transfected cells or cells transfected with pEGFP. The nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to determine significance. *P <.05. (D) NleH inhibits caspase-3 activation in vivo. Colonic sections extracted from mice infected for 9 days with WT or ΔnleH C. rodentium were immunostained with anti–cleaved caspase-3 antibody, anti-intimin antibody (to label bacteria), and Hoechst. Specific caspase-3 activation at bacterial attachment sites was observed in mice infected with ΔnleH mutant, but not in those infected with WT C. rodentium.