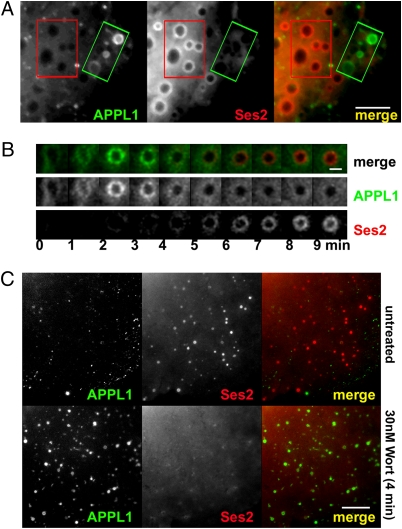
Fig. 6.
APPL1 and Ses2 are localized at different sites along the endocytic pathway. (A) Widefield microscopy of a transfected Cos7 cell showing the different localization of GFP-APPL1–positive and TagRFP-T-Ses2–positive spontaneously occurring macropinosomes. Rectangles define the same regions, primarily occupied by APPL1 vesicles and Ses2 vesicles, respectively, in the two channels. The corresponding movie (Movie S1) shows that GFP-APPL1–positive micropinosomes disappear or mature to become TagRFP-T-Ses2 positive. (Scale bar, 8 μm.) (B) APPL1 precedes Ses2 on the same macropinosome. Selected frames at 1-min intervals of a spinning disk-confocal movie. The micropinosome acquired APPL1, then shed it and acquired Ses2. APPL1 and Ses2 did not overlap. (Scale bar, 2 μm.) (C) The association of Ses2 with endosomes requires the presence of PI3P. Inhibition of PI 3′ kinases with wortmannin induces the dissociation of Ses2 from endosomes which then acquire APPL1. (Scale bar, 10 μm.)