Fig. 2.
hMSCs contribute to in vitro formation of a 3D vascular network within a porous scaffold. (A) The bone scaffold was synthesized of the biocompatible polymer (85∶15) PLGA, by using sucrose leaching to generate interconnected pores averaging 1000 μm. (B) Stable network containing HUVECs and hMSCs in fibronectin-containing collagen gel at 21 days postseeding. (C) Physical interaction of hMSCs with EC network formed in the PLGA scaffold at 28 days postseeding. (D) Relative transcriptional response of the smooth muscle markers smooth muscle actin (ACTA2), calponin (CNN1), SM22 (TAGLN), and smoothelin (SMTN) to the 5-day preconditioning treatment. (E–H) In vitro formation of networks by HUVECs imaged with confocal microscopy at 10 days (E) without hMSCs, (F) with standard condition hMSCs, (G) with hMSCs cultured with TGF-β, and (H) hMSCs cultured in low serum MesenPro medium. (Scale bars: A = 1 mm;  ;
; 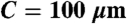 ,
,  . ∗P < 0.05.)
. ∗P < 0.05.)

