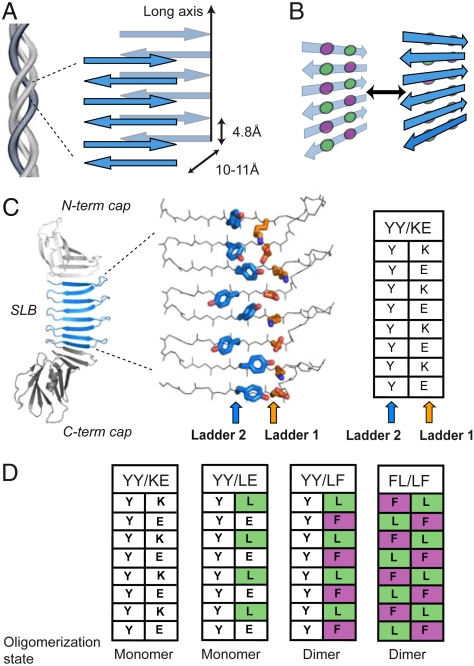
Fig. 1.
The architecture of cross-β fibrils and PSAMs. (A) Diagram of cross-β architecture formed from the lamination of β-sheets. The long-axis and typical distances between intra- and intermolecular β-strands are shown. Though antiparallel β-sheets are shown, cross-β can be formed from either antiparallel or parallel β-sheets. (B) Schematic drawing depicting the concept of cross-strand ladders and the formation of a cross-β dimer from β-sheets containing hydrophobic ladders. Circles denote amino acid side chains that form cross-strand ladders consisting of two amino acid types (colored differently). (C) Left, the PSAM scaffold is shown as a cartoon, with the single-layer β-sheet segment (SLB) colored blue and the N- and C-terminal globular domains colored gray. The side chains of the two cross-strand ladders used as hosts are shown as stick models and colored by element. The carbon atoms of Ladders 1 and 2 are shown in orange and blue, respectively. The table summarizes the amino acid identities of the ladders. (D) Amino acid identities of PSAMs used in this work presented in the table format as in C. Their amino acid sequences are presented in Fig. S1.