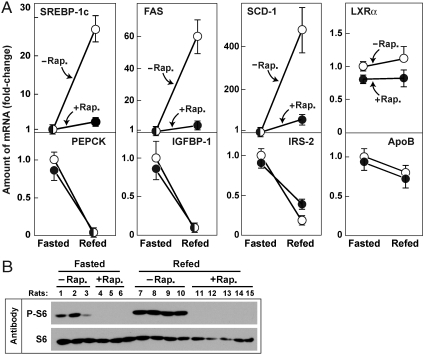
Fig. 3.
Effect of rapamycin on levels of mRNA encoding SREBP-1c and its target genes in livers of rats subjected to fasting and refeeding. Two groups of male Sprague–Dawley rats were fasted for 48 h. Six h prior to sacrifice, one of the groups received an intraperitoneal injection of 20 mg/kg rapamycin (•) and the other group received vehicle (○). One group continued fasting and the other group was refed with a high carbohydrate diet as described in Methods. After 6 h, all animals were anesthesized, and the livers were removed for measurement of mRNAs and phosphorylated proteins. (A) mRNA levels as determined by quantitative RT PCR. Each value represents the amount of mRNA relative to that of the vehicle-treated fasted group that is denoted arbitrarily as one. Values represent mean ± SEM of 3–5 rats in each group. (B) Immunoblot analysis of phosphorylated and total S6 ribosomal protein in livers of the rats used in (A). Filters were exposed to film for 2 sec (P-S6) or 15 sec (S6). Rap., rapamycin. A similar experiment was carried out in mice with similar results, and the experiment in rats was repeated once with similar results.