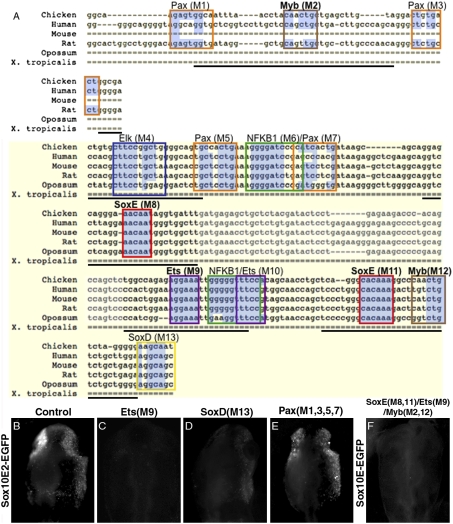
Fig. 3.
Sox10E2 transcriptional inputs. (A) Schematic diagram showing sequence alignment of 264-bp Sox10E2 region; essential core region shaded in yellow. Colored frames indicate computationally identified putative transcription factors binding motifs. Mutations M1 to M13 were replaced by random sequences. Faded sequence shows a 45-bp region deleted or replaced by mCherry coding sequence. Highlighted in blue are conserved nucleotides within putative binding motifs. Single dashed lines indicate absent bases in the alignment and thick dashed lines nonalignable sequences. Thick solid underlines delineate Sox10E2 subfragments used in EMSA and pull-down assays. Sox10E2-driven EGFP expression in CNC (B) is abolished upon mutation of an Ets1 binding motif (C), but only decreased after mutation of putative SoxD motif (D), and not affected by simultaneous mutation of four putative Pax sites (E). (F) Simultaneous inactivation of SoxE, Ets, and Myb binding sites (M2, M8, M9, M11, M12) within a large genomic region abolishes reporter expression in delaminating CNC.