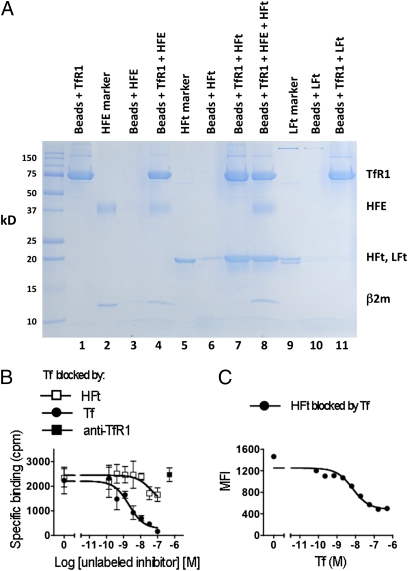
Fig. 2.
Binding of HFt to TfR1 and effects of HFE and Tf. (A) HFt in solution binds to isolated TfR1, and this is not significantly inhibited by HFE. Lanes 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, and 8 show SDS/PAGE of proteins eluted from cobalt beads treated with His-tagged TfR1 only (lane 1), HFE only (lane 3), His-tagged TfR1 followed by HFE (lane 4), HFt only (lane 6), His-tagged TfR1 followed by HFt (lane 7), and His-tagged TfR1 followed by HFE and HFt (HFE:HFt molar ratio = 10:1; lane 8). Lanes 2 and 5 show HFE and HFt, respectively, not exposed to beads but placed directly on the gel. (B) Binding of 125I-Tf to MOLT-4 cells is only partially inhibited by 100× molar excess of HFt (□) and not at all by antibody to TfR1 (■). As a control, binding is inhibited by unlabeled Tf (●). (C) Binding of biotinylated HFt (50 nM) to MOLT-4 cells is inhibited by Tf (●), but inhibition is incomplete, even with a 10-fold molar excess of Tf.