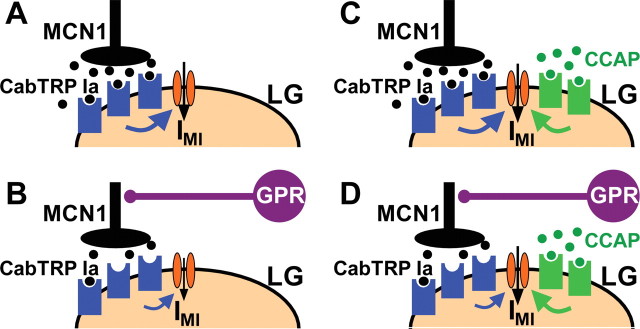
Figure 7.
Summary schematic of the mechanism by which CCAP gates out the GPR regulation of the MCN1–gastric mill rhythm. A, During the normal gastric mill rhythm retractor phase, with no CCAP present, MCN1 released CabTRP Ia (filled black circles) binds to receptors on LG (blue geometric shapes) to activate IMI via an unidentified metabotropic pathway (blue arrow). The downward pointing arrow depicts activated IMI. B, During the gastric mill retractor phase with GPR stimulation and no CCAP present, CabTRP Ia release from MCN1 is reduced, resulting in a reduced rate of activation of IMI (note smaller size of metabotropic- and IMI-associated arrows). C, During the gastric mill retractor phase with CCAP present (filled green circles), IMI in LG is coactivated by MCN1-released CabTRP Ia and bath-applied CCAP. D, During the gastric mill retractor phase with GPR stimulation and CCAP present, GPR still reduces CabTRP Ia release from MCN1. However, because IMI-CCAP in LG is not regulated by GPR activity and can compensate for the reduced amount of IMI-MCN1, the GPR effect on IMI, and hence on the gastric mill retractor phase, is reduced.