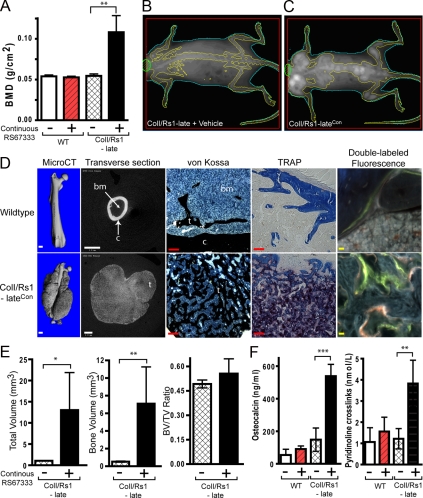
Figure 3.
Continuous ligand activation of Rs1 by RS67333 increases trabecular bone formation. A, Whole-body BMDs as measured by DEXA shows that continuous RS67333 activation of Rs1 increases bone formation in ColI/Rs1–late mice. n = 4 WT + vehicle, 4 WT + RS67333, 4 ColI/Rs1–late + vehicle, 5 ColI/Rs1–late + RS67333 (ColI/Rs1–lateCon mice). WT, wild type. B–C, Representative DEXA images show that ColI/Rs1–lateCon mice have increased bone lesions primarily within the axial skeleton. D, MicroCT, von Kossa, TRAP staining, and fluorescence imaging of femurs from a wild-type mouse treated with RS67333 vs. a ColI/Rs1–lateCon mouse. c, cortical bone; t, trabecular bone; bm, bone marrow space. Scale bars for the CT scan (white), 1 mm; scale bars for von Kossa and TRAP (red), 100 μm; scale bars, double labeled fluorescence imaging (yellow), 10 μm. E, MicroCT quantitation of the 50 midfemur slices for TV, BV, and BV/TV ratio. n = 4 ColI/Rs1–late + vehicle; 5 ColI/Rs1–lateCon mice. Error bars, mean ± 1 sd. F, Serum osteocalcin and pyridinoline cross-link levels. n = 4 WT + vehicle; 4 WT + RS67333; 4 ColI/Rs1–late + vehicle; 5 ColI/Rs1–late + RS67333 (ColI/Rs1–lateCon) mice. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0005.